The ClpS adaptor mediates staged delivery of N-end rule substrates to the AAA+ ClpAP protease
- PMID: 21777811
- PMCID: PMC3168947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.06.009
The ClpS adaptor mediates staged delivery of N-end rule substrates to the AAA+ ClpAP protease
Abstract
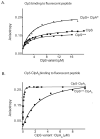
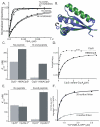
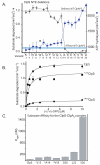
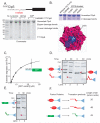
The ClpS adaptor delivers N-end rule substrates to ClpAP, an energy-dependent AAA+ protease, for degradation. How ClpS binds specific N-end residues is known in atomic detail and clarified here, but the delivery mechanism is poorly understood. We show that substrate binding is enhanced when ClpS binds hexameric ClpA. Reciprocally, N-end rule substrates increase ClpS affinity for ClpA(6). Enhanced binding requires the N-end residue and a peptide bond of the substrate, as well as multiple aspects of ClpS, including a side chain that contacts the substrate α-amino group and the flexible N-terminal extension (NTE). Finally, enhancement also needs the N domain and AAA+ rings of ClpA, connected by a long linker. The NTE can be engaged by the ClpA translocation pore, but ClpS resists unfolding/degradation. We propose a staged-delivery model that illustrates how intimate contacts between the substrate, adaptor, and protease reprogram specificity and coordinate handoff from the adaptor to the protease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remodeling of a delivery complex allows ClpS-mediated degradation of N-degron substrates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 16;111(37):E3853-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414933111. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25187555 Free PMC article.
-
ClpS is an essential component of the N-end rule pathway in Escherichia coli.Nature. 2006 Feb 9;439(7077):753-6. doi: 10.1038/nature04412. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16467841
-
The Intrinsically Disordered N-terminal Extension of the ClpS Adaptor Reprograms Its Partner AAA+ ClpAP Protease.J Mol Biol. 2020 Aug 7;432(17):4908-4921. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.07.007. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32687854 Free PMC article.
-
ClpP: a structurally dynamic protease regulated by AAA+ proteins.J Struct Biol. 2012 Aug;179(2):202-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 May 14. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22595189 Review.
-
The N-end rule pathway for regulated proteolysis: prokaryotic and eukaryotic strategies.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;17(4):165-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.02.001. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17306546 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of the LC3B-fusion technique for biochemical and structural studies of proteins involved in the N-degron pathway.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 28;295(9):2590-2600. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010912. Epub 2020 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31919097 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Regulated by UBR Box-Containing E3 Ligases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 3;22(15):8323. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158323. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formyl-methionine as a degradation signal at the N-termini of bacterial proteins.Microb Cell. 2015;2(10):376-393. doi: 10.15698/mic2015.10.231. Microb Cell. 2015. PMID: 26866044 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Thermotolerance of Zymomonas mobilis by Genes for Reactive Oxygen Species-Scavenging Enzymes and Heat Shock Proteins.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 30;10:3073. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03073. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32082264 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering posttranslational proofreading to discriminate nonstandard amino acids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 16;115(3):619-624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715137115. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29301968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Bachmair A, Finley D, Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986;234:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Bolon DN, Grant RA, Baker TA, Sauer RT. Nucleotide-dependent substrate handoff from the SspB adaptor to the AAA+ ClpXP protease. Mol Cell. 2004;16:343–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

