SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) protein, a highly concentrative and broad specific amino acid transporter, is a novel and effective drug target for treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 21771784
- PMCID: PMC3173074
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.229518
SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) protein, a highly concentrative and broad specific amino acid transporter, is a novel and effective drug target for treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
Abstract
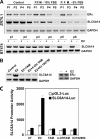
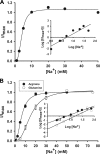
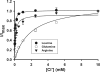
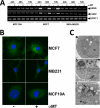
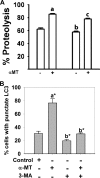
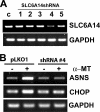
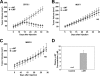
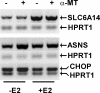
SLC6A14, also known as ATB(0,+), is an amino acid transporter with unique characteristics. It transports 18 of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids. However, this transporter is expressed only at low levels in normal tissues. Here, we show that the transporter is up-regulated specifically in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer, demonstrable with primary human breast cancer tissues and human breast cancer cell lines. SLC6A14 is an estrogen/ER target. The transport features of SLC6A14 include concentrative transport of leucine (an activator of mTOR), glutamine (an essential amino acid for nucleotide biosynthesis and substrate for glutaminolysis), and arginine (an essential amino acid for tumor cells), suggesting that ER-positive breast cancer cells up-regulate SLC6A14 to meet their increased demand for these amino acids. Consequently, treatment of ER-positive breast cancer cells in vitro with α-methyl-DL-tryptophan (α-MT), a selective blocker of SLC6A14, induces amino acid deprivation, inhibits mTOR, and activates autophagy. Prolongation of the treatment with α-MT causes apoptosis. Addition of an autophagy inhibitor (3-methyladenine) during α-MT treatment also induces apoptosis. These effects of α-MT are specific to ER-positive breast cancer cells, which express the transporter. The ability of α-MT to cause amino acid deprivation is significantly attenuated in MCF-7 cells, an ER-positive breast cancer cell line, when SLC6A14 is silenced with shRNA. In mouse xenograft studies, α-MT by itself is able to reduce the growth of the ER-positive ZR-75-1 breast cancer cells. These studies identify SLC6A14 as a novel and effective drug target for the treatment of ER-positive breast cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction of tryptophan derivatives with SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) reveals the potential of the transporter as a drug target for cancer chemotherapy.Biochem J. 2008 Sep 15;414(3):343-55. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080622. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18522536
-
Amino acid transporter SLC6A14 is a novel and effective drug target for pancreatic cancer.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;173(23):3292-3306. doi: 10.1111/bph.13616. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27747870 Free PMC article.
-
SLC6A14, a Na+/Cl--coupled amino acid transporter, functions as a tumor promoter in colon and is a target for Wnt signaling.Biochem J. 2020 Apr 30;477(8):1409-1425. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200099. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32219372 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Transporter SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) - A Target in Combined Anti-cancer Therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 21;8:594464. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.594464. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Na+/Cl--Coupled, Broad-Specific, Amino Acid Transporter SLC6A14 (ATB0,+): Emerging Roles in Multiple Diseases and Therapeutic Potential for Treatment and Diagnosis.AAPS J. 2017 Dec 4;20(1):12. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0164-7. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 29204754 Review.
Cited by
-
18F-Trifluoromethylated D-Cysteine as a Promising New PET Tracer for Glioma Imaging: Comparative Analysis With MRI and Histopathology in Orthotopic C6 Models.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 29;11:645162. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.645162. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996562 Free PMC article.
-
Boronophenylalanine, a boron delivery agent for boron neutron capture therapy, is transported by ATB0,+, LAT1 and LAT2.Cancer Sci. 2015 Mar;106(3):279-86. doi: 10.1111/cas.12602. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25580517 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of the amino acid transporter B0,+ (SLC6A14) to the plasma membrane involves an exclusive interaction with SEC24C for its exit from the endoplasmic reticulum.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Feb;1866(2):252-263. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30445147 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic analysis of the role of solute carrier-glutamine transporters in breast cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(14):777. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2620. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35965834 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-steady-state Kinetic Analysis of Amino Acid Transporter SLC6A14 Reveals Rapid Turnover Rate and Substrate Translocation.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 16;12:777050. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.777050. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34867484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ganapathy V., Inoue K., Prasad P. D., Ganapathy M. E. (2004) in Metabolic and Therapeutic Aspects of Amino Acids in Clinical Nutrition (Cynober L. A. ed) 2nd Ed., pp. 63–78, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
-
- Ganapathy M. E., Ganapathy V. (2005) Curr. Drug Targets Immune Endocr. Metab. Disord. 5, 357–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

