Mesothelial- and epithelial-derived FGF9 have distinct functions in the regulation of lung development
- PMID: 21750028
- PMCID: PMC3188607
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.065110
Mesothelial- and epithelial-derived FGF9 have distinct functions in the regulation of lung development
Abstract
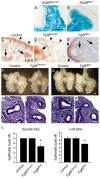
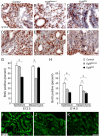
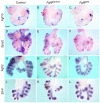
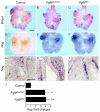
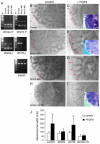
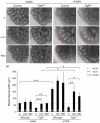
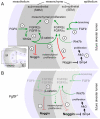
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 9 is a secreted signaling molecule that is expressed in lung mesothelium and epithelium and is required for lung development. Embryos lacking FGF9 show mesenchymal hypoplasia, decreased epithelial branching and, by the end of gestation, hypoplastic lungs that cannot support life. Mesenchymal FGF signaling interacts with β-catenin-mediated WNT signaling in a feed-forward loop that functions to sustain mesenchymal FGF responsiveness and mesenchymal WNT/β-catenin signaling. During pseudoglandular stages of lung development, Wnt2a and Wnt7b are the canonical WNT ligands that activate mesenchymal WNT/β-catenin signaling, whereas FGF9 is the only known ligand that signals to mesenchymal FGF receptors (FGFRs). Here, we demonstrate that mesothelial- and epithelial-derived FGF9, mesenchymal Wnt2a and epithelial Wnt7b have unique functions in lung development in mouse. Mesothelial FGF9 and mesenchymal WNT2A are principally responsible for maintaining mesenchymal FGF-WNT/β-catenin signaling, whereas epithelial FGF9 primarily affects epithelial branching. We show that FGF signaling is primarily responsible for regulating mesenchymal proliferation, whereas β-catenin signaling is a required permissive factor for mesenchymal FGF signaling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 9 expression and FGF-WNT/β-catenin signaling in laser-induced wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2014 Sep-Oct;22(5):660-5. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12212. Wound Repair Regen. 2014. PMID: 25041895
-
FGF9 and FGF10 activate distinct signaling pathways to direct lung epithelial specification and branching.Sci Signal. 2020 Mar 3;13(621):eaay4353. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aay4353. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32127497 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal epithelial-mesenchymal FGF signaling is required for cecal development.Development. 2006 Jan;133(1):173-80. doi: 10.1242/dev.02175. Epub 2005 Nov 24. Development. 2006. PMID: 16308329 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk of WNT and FGF signaling pathways at GSK3beta to regulate beta-catenin and SNAIL signaling cascades.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Sep;5(9):1059-64. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.9.3151. Epub 2006 Sep 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16940750 Review.
-
Tissue crosstalk in lung development.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Sep;115(9):1469-77. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24811. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24644090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling networks regulating development of the lower respiratory tract.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 May 1;4(5):a008318. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008318. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22550231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt and FGF mediated epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk during lung development.Dev Dyn. 2015 Mar;244(3):342-66. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24234. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Dev Dyn. 2015. PMID: 25470458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 Regulation by MicroRNAs Controls Lung Development and Links DICER1 Loss to the Pathogenesis of Pleuropulmonary Blastoma.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 15;11(5):e1005242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005242. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25978641 Free PMC article.
-
FGF9 Alleviates the Fatty Liver Phenotype by Regulating Hepatic Lipid Metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 20;13:850128. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.850128. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35517790 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Tg(Etv4-GFP) and Etv5 RFP Reporter Lines in the Context of Fibroblast Growth Factor 10 Signaling During Mouse Embryonic Lung Development.Front Genet. 2019 Mar 14;10:178. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00178. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30923534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellusci S., Henderson R., Winnier G., Oikawa T., Hogan B. L. (1996). Evidence from normal expression and targeted misexpression that bone morphogenetic protein (Bmp-4) plays a role in mouse embryonic lung morphogenesis. Development 122, 1693-1702 - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S., Grindley J., Emoto H., Itoh N., Hogan B. L. (1997). Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development 124, 4867-4878 - PubMed
-
- Colvin J. S., Feldman B., Nadeau J. H., Goldfarb M., Ornitz D. M. (1999). Genomic organization and embryonic expression of the mouse fibroblast growth factor 9 gene. Dev. Dyn. 216, 72-88 - PubMed
-
- Colvin J. S., White A., Pratt S. J., Ornitz D. M. (2001a). Lung hypoplasia and neonatal death in Fgf9-null mice identify this gene as an essential regulator of lung mesenchyme. Development 128, 2095-2106 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

