Myocardial AKT: the omnipresent nexus
- PMID: 21742795
- PMCID: PMC3674828
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00024.2010
Myocardial AKT: the omnipresent nexus
Abstract
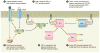
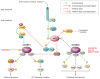
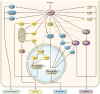
One of the greatest examples of integrated signal transduction is revealed by examination of effects mediated by AKT kinase in myocardial biology. Positioned at the intersection of multiple afferent and efferent signals, AKT exemplifies a molecular sensing node that coordinates dynamic responses of the cell in literally every aspect of biological responses. The balanced and nuanced nature of homeostatic signaling is particularly essential within the myocardial context, where regulation of survival, energy production, contractility, and response to pathological stress all flow through the nexus of AKT activation or repression. Equally important, the loss of regulated AKT activity is primarily the cause or consequence of pathological conditions leading to remodeling of the heart and eventual decompensation. This review presents an overview compendium of the complex world of myocardial AKT biology gleaned from more than a decade of research. Summarization of the widespread influence that AKT exerts upon myocardial responses leaves no doubt that the participation of AKT in molecular signaling will need to be reckoned with as a seemingly omnipresent regulator of myocardial molecular biological responses.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial integrity: preservation through Akt/Pim-1 kinase signaling in the cardiomyocyte.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009 Aug;7(8):929-38. doi: 10.1586/erc.09.48. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009. PMID: 19673671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIM kinase (and Akt) biology and signaling in tumors.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jul;151:41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25749412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream.Cell. 2007 Jun 29;129(7):1261-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17604717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotection induced by hydrogen sulfide preconditioning involves activation of ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Jan;455(4):607-16. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0321-4. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 17674030
-
Myocardial protection by insulin at reperfusion requires early administration and is mediated via Akt and p70s6 kinase cell-survival signaling.Circ Res. 2001 Dec 7;89(12):1191-8. doi: 10.1161/hh2401.101385. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11739285
Cited by
-
METTL14 is required for exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy and protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 9;13(1):6762. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34434-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36351918 Free PMC article.
-
Plin5, a New Target in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:2122856. doi: 10.1155/2022/2122856. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35509833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Oct 22;13:142. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0142-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 25338737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of JAK1 by RNA interference inhibits growth of the lung cancer cell line A549 and interferes with the PI3K/mTOR pathway.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011 Nov;137(11):1629-40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1037-6. Epub 2011 Aug 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21861134
-
Heterozygous deletion of AKT1 rescues cardiac contractility, but not hypertrophy, in a mouse model of Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Lentigines.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Nov;112:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28911943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abete P, Testa G, Ferrara N, De Santis D, Capaccio P, Viati L, Calabrese C, Cacciatore F, Longobardi G, Condorelli M, Napoli C, Rengo F. Cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning is preserved in food-restricted senescent rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282:H1978–H1987. - PubMed
-
- Abid MR, Guo S, Minami T, Spokes KC, Ueki K, Skurk C, Walsh K, Aird WC. Vascular endothelial growth factor activates PI3K/Akt/forkhead signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:294–300. - PubMed
-
- Adams JW, Pagel AL, Means CK, Oksenberg D, Armstrong RC, Brown JH. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by Galphaq signaling is mediated by permeability transition pore formation and activation of the mitochondrial death pathway. Circ Res. 2000;87:1180–1187. - PubMed
-
- Agata J, Chao L, Chao J. Kallikrein gene delivery improves cardiac reserve and attenuates remodeling after myocardial infarction. Hypertension. 2002;40:653–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01HL085577-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R21 HL104544-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL100891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL091102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IR37 HL091102-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL102714/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R01HL067245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21HL102714-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL085577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL104544/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL102613/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1HL100891-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL102613-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

