Rapid evolutionary rewiring of a structurally constrained eye enhancer
- PMID: 21737276
- PMCID: PMC3143281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.05.056
Rapid evolutionary rewiring of a structurally constrained eye enhancer
Abstract
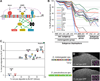
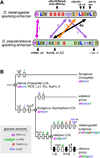
Background: Enhancers are genomic cis-regulatory sequences that integrate spatiotemporal signals to control gene expression. Enhancer activity depends on the combination of bound transcription factors as well as-in some cases-the arrangement and spacing of binding sites for these factors. Here, we examine evolutionary changes to the sequence and structure of sparkling, a Notch/EGFR/Runx-regulated enhancer that activates the dPax2 gene in cone cells of the developing Drosophila eye.
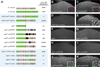
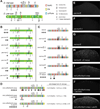
Results: Despite functional and structural constraints on its sequence, sparkling has undergone major reorganization in its recent evolutionary history. Our data suggest that the relative strengths of the various regulatory inputs into sparkling change rapidly over evolutionary time, such that reduced input from some factors is compensated by increased input from different regulators. These gains and losses are at least partly responsible for the changes in enhancer structure that we observe. Furthermore, stereotypical spatial relationships between certain binding sites ("grammar elements") can be identified in all sparkling orthologs-although the sites themselves are often recently derived. We also find that low binding affinity for the Notch-regulated transcription factor Su(H), a conserved property of sparkling, is required to prevent ectopic responses to Notch in noncone cells.
Conclusions: Rapid DNA sequence turnover does not imply either the absence of critical cis-regulatory information or the absence of structural rules. Our findings demonstrate that even a severely constrained cis-regulatory sequence can be significantly rewired over a short evolutionary timescale.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Gene regulation: piecing together the puzzle of enhancer evolution.Curr Biol. 2011 Jul 26;21(14):R542-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.026. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21783031
Similar articles
-
Structural rules and complex regulatory circuitry constrain expression of a Notch- and EGFR-regulated eye enhancer.Dev Cell. 2010 Mar 16;18(3):359-70. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.12.026. Dev Cell. 2010. PMID: 20230745 Free PMC article.
-
Sparkling insights into enhancer structure, function, and evolution.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;98:97-120. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386499-4.00004-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22305160 Review.
-
Combinatorial signaling by the Frizzled/PCP and Egfr pathways during planar cell polarity establishment in the Drosophila eye.Dev Biol. 2008 Apr 1;316(1):110-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.016. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18291359 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme Usp5 regulates Notch and RTK signaling during Drosophila eye development.FEBS Lett. 2017 Mar;591(6):875-888. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12580. Epub 2017 Mar 6. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28140449
-
Selector and signalling molecules cooperate in organ patterning.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;4(3):E48-51. doi: 10.1038/ncb0302-e48. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11875444 Review.
Cited by
-
Tempo and mode in evolution of transcriptional regulation.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002432. Epub 2012 Jan 19. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22291600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Structural and Biochemical Insights into Shape, Sugar, and Force.Dev Cell. 2017 May 8;41(3):228-241. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.04.001. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28486129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extensive divergence of transcription factor binding in Drosophila embryos with highly conserved gene expression.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(9):e1003748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003748. Epub 2013 Sep 12. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24068946 Free PMC article.
-
Different Evolutionary Strategies To Conserve Chromatin Boundary Function in the Bithorax Complex.Genetics. 2017 Feb;205(2):589-603. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.195586. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28007886 Free PMC article.
-
Role of architecture in the function and specificity of two Notch-regulated transcriptional enhancer modules.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jul;8(7):e1002796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002796. Epub 2012 Jul 5. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22792075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giese K, Kingsley C, Kirshner JR, Grosschedl R. Assembly and function of a TCR enhancer complex is dependent on LEF-1-induced DNA bending and multiple protein-protein interactions. Genes Dev. 1995;9:995–1008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

