Regulation of gene expression in plants through miRNA inactivation
- PMID: 21731706
- PMCID: PMC3121747
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021330
Regulation of gene expression in plants through miRNA inactivation
Abstract
Eukaryotic organisms possess a complex RNA-directed gene expression regulatory network allowing the production of unique gene expression patterns. A recent addition to the repertoire of RNA-based gene regulation is miRNA target decoys, endogenous RNA that can negatively regulate miRNA activity. miRNA decoys have been shown to be a valuable tool for understanding the function of several miRNA families in plants and invertebrates. Engineering and precise manipulation of an endogenous RNA regulatory network through modification of miRNA activity also affords a significant opportunity to achieve a desired outcome of enhanced plant development or response to environmental stresses. Here we report that expression of miRNA decoys as single or heteromeric non-cleavable microRNA (miRNA) sites embedded in either non-protein-coding or within the 3' untranslated region of protein-coding transcripts can regulate the expression of one or more miRNA targets. By altering the sequence of the miRNA decoy sites, we were able to attenuate miRNA inactivation, which allowed for fine regulation of native miRNA targets and the production of a desirable range of plant phenotypes. Thus, our results demonstrate miRNA decoys are a flexible and robust tool, not only for studying miRNA function, but also for targeted engineering of gene expression in plants. Computational analysis of the Arabidopsis transcriptome revealed a number of potential miRNA decoys, suggesting that endogenous decoys may have an important role in natural modulation of expression in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



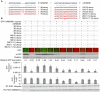
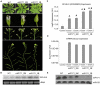
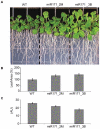
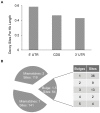
Similar articles
-
RNA decoys: an emerging component of plant regulatory networks?Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Sep 1;7(9):1188-93. doi: 10.4161/psb.21299. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22899065 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient silencing of endogenous microRNAs using artificial microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant. 2011 Jan;4(1):157-70. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq061. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 20943811
-
The Use of MicroRNA Decoy Technologies to Inhibit miRNA Function in Arabidopsis.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1932:227-238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9042-9_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30701504
-
Mobile plant microRNAs allow communication within and between organisms.New Phytol. 2022 Sep;235(6):2176-2182. doi: 10.1111/nph.18360. Epub 2022 Jul 20. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35794849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The function of RNAi in plant development.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:165-70. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.030. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381293 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA decoys: an emerging component of plant regulatory networks?Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Sep 1;7(9):1188-93. doi: 10.4161/psb.21299. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22899065 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biochemical insights into small RNA 3' end trimming by Arabidopsis SDN1.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 4;9(1):3585. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05942-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30181559 Free PMC article.
-
PAREameters: a tool for computational inference of plant miRNA-mRNA targeting rules using small RNA and degradome sequencing data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Mar 18;48(5):2258-2270. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1234. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31943065 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of rice root development by a retrotransposon acting as a microRNA sponge.Elife. 2017 Aug 26;6:e30038. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30038. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28847366 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of microRNA turnover.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015 Oct;27:199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.07.008. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26342825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B. MicroRNAS and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:19–53. - PubMed
-
- Shukla LI, Chinnusamy V, Sunkar R. The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779:743–748. - PubMed
-
- Llave C, Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC. Cleavage of Scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science. 2002;297:2053–2056. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

