Small-molecule inhibitor binding to an N-acyl-homoserine lactone synthase
- PMID: 21730159
- PMCID: PMC3141922
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1103165108
Small-molecule inhibitor binding to an N-acyl-homoserine lactone synthase
Abstract
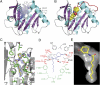
Quorum sensing (QS) controls certain behaviors of bacteria in response to population density. In gram-negative bacteria, QS is often mediated by N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (acyl-HSLs). Because QS influences the virulence of many pathogenic bacteria, synthetic inhibitors of acyl-HSL synthases might be useful therapeutically for controlling pathogens. However, rational design of a potent QS antagonist has been thwarted by the lack of information concerning the binding interactions between acyl-HSL synthases and their ligands. In the gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia glumae, QS controls virulence, motility, and protein secretion and is mediated by the binding of N-octanoyl-L-HSL (C8-HSL) to its cognate receptor, TofR. C8-HSL is synthesized by the acyl-HSL synthase TofI. In this study, we characterized two previously unknown QS inhibitors identified in a focused library of acyl-HSL analogs. Our functional and X-ray crystal structure analyses show that the first inhibitor, J8-C8, binds to TofI, occupying the binding site for the acyl chain of the TofI cognate substrate, acylated acyl-carrier protein. Moreover, the reaction byproduct, 5'-methylthioadenosine, independently binds to the binding site for a second substrate, S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Closer inspection of the mode of J8-C8 binding to TofI provides a likely molecular basis for the various substrate specificities of acyl-HSL synthases. The second inhibitor, E9C-3oxoC6, competitively inhibits C8-HSL binding to TofR. Our analysis of the binding of an inhibitor and a reaction byproduct to an acyl-HSL synthase may facilitate the design of a new class of QS-inhibiting therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
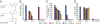
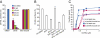

Similar articles
-
The Complex Quorum Sensing Circuitry of Burkholderia thailandensis Is Both Hierarchically and Homeostatically Organized.mBio. 2017 Dec 5;8(6):e01861-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01861-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29208745 Free PMC article.
-
Two rsaM Homologues Encode Central Regulatory Elements Modulating Quorum Sensing in Burkholderia thailandensis.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 25;200(14):e00727-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00727-17. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29507087 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual multiple production of N-acylhomoserine lactones a by Burkholderia sp. strain C10B isolated from dentine caries.Sensors (Basel). 2014 May 21;14(5):8940-9. doi: 10.3390/s140508940. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24854358 Free PMC article.
-
Variations on a theme: diverse N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing mechanisms in gram-negative bacteria.Sci Prog. 2006;89(Pt 3-4):167-211. doi: 10.3184/003685006783238335. Sci Prog. 2006. PMID: 17338438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing.Annu Rev Genet. 2001;35:439-68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.35.102401.090913. Annu Rev Genet. 2001. PMID: 11700290 Review.
Cited by
-
N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Analog Modulators of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Rhll Quorum Sensing Signal Synthase.ACS Chem Biol. 2019 Oct 18;14(10):2305-2314. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00671. Epub 2019 Oct 9. ACS Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31545595 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotargeting of Resistant Infections with a Special Emphasis on the Biofilm Landscape.Bioconjug Chem. 2021 Aug 18;32(8):1411-1430. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00116. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Bioconjug Chem. 2021. PMID: 34319073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saline Environments as a Source of Potential Quorum Sensing Disruptors to Control Bacterial Infections: A Review.Mar Drugs. 2019 Mar 25;17(3):191. doi: 10.3390/md17030191. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30934619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target.Sci Rep. 2014 Nov 28;4:7245. doi: 10.1038/srep07245. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25430794 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing: how bacteria can coordinate activity and synchronize their response to external signals?Protein Sci. 2012 Oct;21(10):1403-17. doi: 10.1002/pro.2132. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22825856 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fuqua C, Greenberg EP. Listening in on bacteria: Acyl-homoserine lactone signaling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:685–695. - PubMed
-
- Waters CM, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:319–346. - PubMed
-
- Moré MI, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of a quorum-sensing autoinducer through use of defined substrates. Science. 1996;272:1655–1658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

