Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy
- PMID: 21725353
- PMCID: PMC3356932
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.267
Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy
Abstract
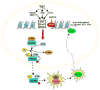
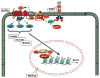
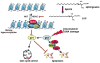
The class-I histone deacetylases (HDACs) HDAC1 and HDAC2 belong to a family of 11 zinc-dependent human HDACs and are overexpressed in many cancers. Inhibitors of these HDACs now in clinical trials show activity against several types of cancers. This review is focused on recent advances in both clinical and preclinical efforts to understand the basis for the actions of HDACis, with emphasis on implications for rational combinations with conventional or other targeted agents. We will address new perspectives on the molecular mechanisms by which HDACs act and how these actions relate to cancer. We will also review new evidence showing that HDACs are direct intracellular targets of the potent sphingolipid mediator S1P, the first identified endogenous nuclear regulator of these enzymes, linking sphingolipid metabolism in the nucleus to remodeling of chromatin and epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Understanding how endogenous molecules regulate HDAC activity in vivo may facilitate the search for safer and more effective anticancer drugs capable of interfering with HDAC functions in a highly specific manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
New endogenous regulators of class I histone deacetylases.Sci Signal. 2010 Jan 5;3(103):pe1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3103pe1. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20051592 Review.
-
Pharmacological or transcriptional inhibition of both HDAC1 and 2 leads to cell cycle blockage and apoptosis via p21Waf1/Cip1 and p19INK4d upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Prolif. 2018 Jun;51(3):e12447. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12447. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 29484736 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and 2 expression and chemotherapy in gastric cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2010 Dec;17(12):3336-43. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1182-1. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20585871
-
Molecular and biologic analysis of histone deacetylase inhibitors with diverse specificities.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Dec;12(12):2709-21. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0626. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 24092806
-
The Search for Potent, Small-Molecule HDACIs in Cancer Treatment: A Decade After Vorinostat.Med Res Rev. 2017 Nov;37(6):1373-1428. doi: 10.1002/med.21437. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Med Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28181261 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors as radiosensitisers: effects on DNA damage signalling and repair.Br J Cancer. 2013 Mar 5;108(4):748-54. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.21. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23361058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol induces epigenetic modulation of prodynorphin and pronociceptin gene expression in the rat amygdala complex.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Feb;49(2):312-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9829-y. Epub 2012 Jun 10. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22684622
-
Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Aug;87(8):1315-530. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1078-5. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23974980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin remodeling: a new landscape to treat harmful alcohol-use disorders.Future Med Chem. 2013 Nov;5(17):2011-3. doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.152. Future Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24215342 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mitochondria in cancer.Cell Stress. 2020 May 11;4(6):114-146. doi: 10.15698/cst2020.06.221. Cell Stress. 2020. PMID: 32548570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albi E, Lazzarini R, Viola Magni M. Phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin metabolism crosstalk inside the nucleus. Biochem J. 2008;410:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Almenara J, Rosato R, Grant S. Synergistic induction of mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells by flavopiridol and the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) Leukemia. 2002;16:1331–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bali P, George P, Cohen P, Tao J, Guo F, Sigua C, et al. Superior activity of the combination of histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 and the FLT-3 kinase inhibitor PKC412 against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells with mutant FLT-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4991–4997. - PubMed
-
- Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26729–26734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37GM043880/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2CA148431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA142509/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19AI077435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA100866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA93738-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21CA137823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P50CA130805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM043880/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA137823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA61774/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093738/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P50CA142509/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA061774/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM043880/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA130805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI50094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

