Immunity against Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infections
- PMID: 21720387
- PMCID: PMC5868361
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3010
Immunity against Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infections
Abstract
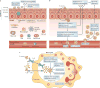
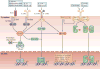
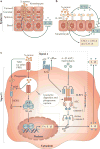
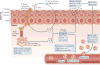
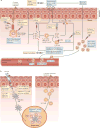
Complications arising from cutaneous and soft tissue infections with Staphylococcus aureus are a major clinical problem owing to the high incidence of these infections and the widespread emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. If prophylactic vaccines or immunotherapy for certain patient populations are to be developed as an alternative to antibiotics, it will be essential to better understand the immune mechanisms that provide protection against S. aureus skin infections. Recent discoveries have identified a key role for interleukin-1 (IL-1)- and IL-17-mediated immune responses in promoting neutrophil recruitment to the site of infection in the skin, a process that is required for host defence and bacterial clearance. This Review describes these new insights and discusses their potential impact on immune-based therapies and vaccination strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate and adaptive immune responses against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections.Semin Immunopathol. 2012 Mar;34(2):261-80. doi: 10.1007/s00281-011-0292-6. Epub 2011 Nov 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22057887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17 is essential for host defense against cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice.J Clin Invest. 2010 May;120(5):1762-73. doi: 10.1172/JCI40891. Epub 2010 Apr 1. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20364087 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-derived IL-1β is sufficient for abscess formation in immunity against Staphylococcus aureus in mice.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1003047. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003047. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23209417 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Mediated Protection against Staphylococcus aureus Dermonecrosis: Synergy of Toxin Neutralization and Neutrophil Recruitment.J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Apr;141(4):810-820.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 16. J Invest Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32946878 Free PMC article.
-
Host-pathogen interactions between the skin and Staphylococcus aureus.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012 Feb;15(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22137885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Improves Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Infections From Abscess Specimens: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 15;11:2034. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02034. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042033 Free PMC article.
-
Diversified Stimuli-Induced Inflammatory Pathways Cause Skin Pigmentation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 12;22(8):3970. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083970. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IL-20 cytokine subfamily: bad guys in host defense?Nat Immunol. 2013 Aug;14(8):774-5. doi: 10.1038/ni.2664. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23867927 No abstract available.
-
Mucosa-Associated Invariant T Cell Hypersensitivity to Staphylococcus aureus Leukocidin ED and Its Modulation by Activation.J Immunol. 2022 Mar 1;208(5):1170-1179. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100912. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35140134 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profile Analyses of the Skin Response of Balb/c-Nu Mice Model Injected by Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022 Feb 15;15:217-235. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S348961. eCollection 2022. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35210800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moran GJ, et al. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:666–674. - PubMed
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;339:520–532. - PubMed
-
- Daum RS. Clinical practice. Skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007;357:380–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

