MMP-mediated disruption of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier of rat brain after cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 21717368
- PMCID: PMC4950933
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-61779-185-7_24
MMP-mediated disruption of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier of rat brain after cerebral ischemia
Abstract
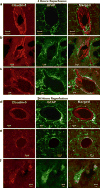
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) has become a major focus of attention in cerebral pathophysiology and disease progression in the central nervous system. Endothelial tight junctions, the basal lamina, and perivascular astrocytes are jointly referred to as BBB or neurovascular unit. Around the cerebral endothelial cells is the basal lamina composed primarily of laminin, fibronectin, and heparan sulfate. The basal lamina provides a structural barrier to extravasation of cellular blood elements and anchors endothelial cells to astrocytes. Barriers limiting transport into and out of the brain are found at the tight junction proteins and at the basal lamina. The relative contribution of these two sites has not been studied, but it is likely that both are disrupted to some extent in various injury scenarios. We have shown that activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) opens the BBB by degrading tight junction proteins (claudin-5 and occludin) and increases BBB permeability after stroke, and that an MMP inhibitor prevents degradation of tight junction proteins and attenuates BBB disruption.
Figures
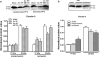
Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Apr;27(4):697-709. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600375. Epub 2006 Jul 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 16850029
-
Specific role of tight junction proteins claudin-5, occludin, and ZO-1 of the blood-brain barrier in a focal cerebral ischemic insult.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Jun;44(2):130-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9496-4. Epub 2011 Feb 12. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21318404
-
Partial recovery of the damaged rat blood-brain barrier is mediated by adherens junction complexes, extracellular matrix remodeling and macrophage infiltration following focal astrocyte loss.Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 10;250:773-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.06.061. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23845748 Free PMC article.
-
Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia.Neurosurg Focus. 2007 May 15;22(5):E4. doi: 10.3171/foc.2007.22.5.5. Neurosurg Focus. 2007. PMID: 17613235 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):C343-C356. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29949404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection induces MMP-9 and causes tight junction protein disruption associated with Purkinje cell degeneration.Parasitol Res. 2020 Oct;119(10):3433-3441. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06840-y. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32789733
-
Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood-Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model.Appl Sci (Basel). 2024 May 1;14(9):3917. doi: 10.3390/app14093917. Epub 2024 May 4. Appl Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39027034 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RNS/caveolin-1/MMP signaling cascades to protect against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injuries: potential application for drug discovery.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 May;39(5):669-682. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.27. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29595191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Venous endothelial injury in central nervous system diseases.BMC Med. 2013 Oct 11;11:219. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-219. BMC Med. 2013. PMID: 24228622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho kinase: A new target for treatment of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013 May 5;8(13):1180-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.13.003. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173–85. - PubMed
-
- Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Liebner S, et al. Correlation of tight junction morphology with the expression of tight junction proteins in blood-brain barrier endothelial cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2000;79(10):707–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

