Vascular β-amyloid and early astrocyte alterations impair cerebrovascular function and cerebral metabolism in transgenic arcAβ mice
- PMID: 21688176
- PMCID: PMC3168476
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-011-0834-y
Vascular β-amyloid and early astrocyte alterations impair cerebrovascular function and cerebral metabolism in transgenic arcAβ mice
Abstract
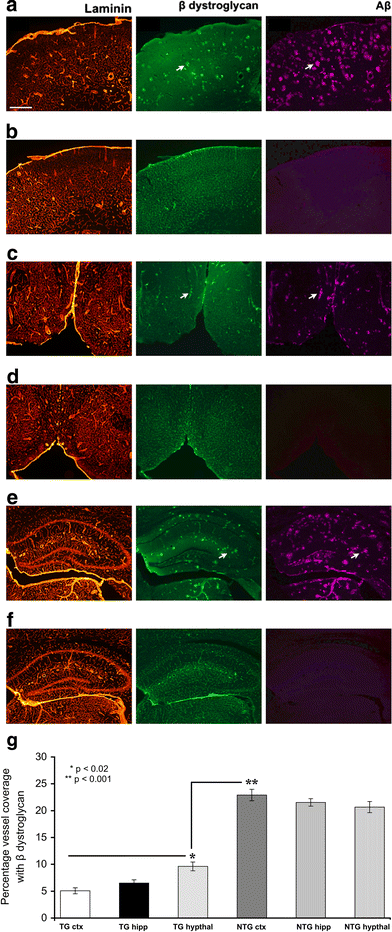
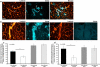
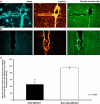
Cerebrovascular lesions related to congophilic amyloid angiopathy (CAA) often accompany deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) in Alzheimer's disease (AD), leading to disturbed cerebral blood flow and cognitive dysfunction, posing the question how cerebrovascular pathology contributes to the pathology of AD. To address this question, we characterised the morphology, biochemistry and functionality of brain blood vessels in transgenic arctic β-amyloid (arcAβ) mice expressing human amyloid precursor protein (APP) with both the familial AD-causing Swedish and Arctic mutations; these mice are characterised by strong CAA pathology. Mice were analysed at early, mid and late-stage pathology. Expression of the glucose transporter GLUT1 at the blood-brain barrier (BBB) was significantly decreased and paralleled by impaired in vivo blood-to-brain glucose transport and reduced cerebral lactate release during neuronal activation from mid-stage pathology onwards. Reductions in astrocytic GLUT1 and lactate transporters, as well as retraction of astrocyte endfeet and swelling consistent with neurovascular uncoupling, preceded wide-spread β-amyloid plaque pathology. We show that CAA at later disease stages is accompanied by severe morphological alterations of brain blood vessels including stenoses, BBB leakages and the loss of vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs). Together, our data establish that cerebrovascular and astrocytic pathology are paralleled by impaired cerebral metabolism in arcAβ mice, and that astrocyte alterations occur already at premature stages of pathology, suggesting that astrocyte dysfunction can contribute to early behavioural and cognitive impairments seen in these mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ApoA-I deficiency increases cortical amyloid deposition, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cortical and hippocampal astrogliosis, and amyloid-associated astrocyte reactivity in APP/PS1 mice.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 May 13;11(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0497-9. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31084613 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular mechanisms and blood-brain barrier disorder in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Jul;118(1):103-13. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0522-3. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Acta Neuropathol. 2009. PMID: 19319544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Impaired Cerebrovascular Structure in APP/PS1 Mouse Brains.Neuroscience. 2018 Aug 10;385:246-254. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 17. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29777753
-
Reduced nitric oxide bioavailability mediates cerebroarterial dysfunction independent of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Feb 1;312(2):H232-H238. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00607.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27836896
-
Hereditary and sporadic forms of abeta-cerebrovascular amyloidosis and relevant transgenic mouse models.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 Apr 23;10(4):1872-1895. doi: 10.3390/ijms10041872. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19468344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Human BBB-on-a-Chip: A New Platform for Alzheimer's Disease Studies.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Aug;10(15):e2002285. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202002285. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 34075728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Targeting of the Neurovascular Unit: Challenges and Advancements.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;42(7):2131-2146. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01113-3. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34086179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statins Inhibit Fibrillary β-Amyloid Induced Inflammation in a Model of the Human Blood Brain Barrier.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157483. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27309956 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection in early stages of Alzheimer's disease is promoted by transthyretin angiogenic properties.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Aug 24;13(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00883-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34429155 Free PMC article.
-
Grey matter ageing-related tau astrogliopathy: associations with brain pathologies and cognitive decline.Brain. 2024 Oct 3;147(10):3501-3512. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae250. Brain. 2024. PMID: 39045644
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

