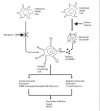
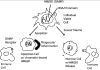
Trauma is danger
- PMID: 21676213
- PMCID: PMC3131254
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-92
Trauma is danger
Abstract
Background: Trauma is one of the leading causes of death in young adult patients. Many pre-clinical and clinical studies attempt to investigate the immunological pathways involved, however the true mediators remain to be elucidated. Herein, we attempt to describe the immunologic response to systemic trauma in the context of the Danger model.
Data sources: A literature search using PubMed was used to identify pertinent articles describing the Danger model in relation to trauma.
Conclusions: Our knowledge of Danger signals in relation to traumatic injury is still limited. Danger/alarmin signals are the most proximal molecules in the immune response that have many possibilities for effector function in the innate and acquired immune systems. Having a full understanding of these molecules and their pathways would give us the ability to intervene at such an early stage and may prove to be more effective in blunting the post-injury inflammatory response unlike previously failed cytokine experiments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Danger signals from mitochondrial DAMPS in trauma and post-injury sepsis.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018 Jun;44(3):317-324. doi: 10.1007/s00068-018-0963-2. Epub 2018 May 24. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018. PMID: 29797026 Review.
-
Innate danger signals in acute injury: From bench to bedside.Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2016 Aug;35(4):283-92. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2015.10.009. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2016. PMID: 26987739 Review.
-
Trauma equals danger--damage control by the immune system.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Sep;92(3):539-51. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212072. Epub 2012 May 31. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22654121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danger signals activating the immune response after trauma.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:315941. doi: 10.1155/2012/315941. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 22778496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danger Signals in the ICU.Crit Care Med. 2018 May;46(5):791-798. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003007. Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29443814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects and mechanisms of chinese herbal medicine in ameliorating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:925625. doi: 10.1155/2013/925625. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24288571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute muscle mass loss was alleviated with HMGB1 neutralizing antibody treatment in severe burned rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 24;13(1):10250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37476-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37355693 Free PMC article.
-
Alarming Cargo: The Role of Exosomes in Trauma-Induced Inflammation.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 31;11(4):522. doi: 10.3390/biom11040522. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33807302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid systemic surge of IL-33 after severe human trauma: a prospective observational study.Mol Med. 2021 Mar 26;27(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00288-1. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33771098 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of innate immunity by extracellular nucleotides.Am J Blood Res. 2013;3(1):14-28. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Am J Blood Res. 2013. PMID: 23358447 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical