Distribution of Bim determines Mcl-1 dependence or codependence with Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 in Mcl-1-expressing myeloma cells
- PMID: 21659544
- PMCID: PMC3152498
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-327197
Distribution of Bim determines Mcl-1 dependence or codependence with Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 in Mcl-1-expressing myeloma cells
Abstract
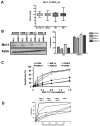
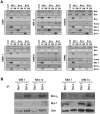
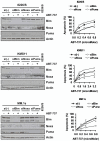
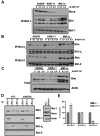
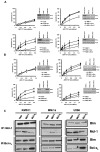
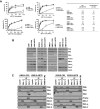
Dependence on Bcl-2 proteins is a common feature of cancer cells and provides a therapeutic opportunity. ABT-737 is an antagonist of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and therefore is a good predictor of Bcl-x(L)/Bcl-2 dependence. Surprisingly, analysis of Mcl-1-dependent multiple myeloma cell lines revealed codependence on Bcl-2/Bcl-x(L) in half the cells tested. Codependence is not predicted by the expression level of antiapoptotic proteins, rather through interactions with Bim. Consistent with these findings, acquired resistance to ABT-737 results in loss of codependence through redistribution of Bim to Mcl-1. Overall, these results suggest that complex interactions, and not simply expression patterns of Bcl-2 proteins, need to be investigated to understand Bcl-2 dependence and how to better use agents, such as ABT-737.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bim upregulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors mediates interactions with the Bcl-2 antagonist ABT-737: evidence for distinct roles for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(23):6149-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01481-08. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19805519 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL strikingly enhances PI3K inhibition-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a GSK3- and Bim-dependent mechanism.Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 15;73(4):1340-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1365. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23243017 Free PMC article.
-
Mcl-1 Phosphorylation defines ABT-737 resistance that can be overcome by increased NOXA expression in leukemic B cells.Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 15;72(12):3069-79. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-4106. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22525702 Free PMC article.
-
Mcl-1 is a potential therapeutic target in multiple types of cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Apr;66(8):1326-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8637-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19099185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding and unlocking the BCL-2 dependency of cancer cells.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Jul;13(7):455-65. doi: 10.1038/nrc3538. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23783119 Review.
Cited by
-
BCL2-BH4 antagonist BDA-366 suppresses human myeloma growth.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27753-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8513. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27049723 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-2 family proteins in breast development and cancer: could Mcl-1 targeting overcome therapeutic resistance?Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3519-30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2792. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25784482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous modulation of Bcl-2 family members and drug efflux mediate MCL-1 inhibitor resistance in multiple myeloma.Blood Adv. 2021 Oct 26;5(20):4125-4139. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003826. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 34478517 Free PMC article.
-
Found in Translation: How Preclinical Research Is Guiding the Clinical Development of the BCL2-Selective Inhibitor Venetoclax.Cancer Discov. 2017 Dec;7(12):1376-1393. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0797. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 29146569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low expression of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins sets the apoptotic threshold in Waldenström macroglobulinemia.Oncogene. 2016 Jan 28;35(4):479-90. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.103. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25893290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuroda J, Taniwaki M. Involvement of BH3-only proteins in hematologic malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;71(2):89–101. - PubMed
-
- Hacker G, Weber A. BH3-only proteins trigger cytochrome c release, but how? Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;462(2):150–155. - PubMed
-
- Willis SN, Fletcher JI, Kaufmann T, et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science. 2007;315(5813):856–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

