CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis
- PMID: 21654748
- PMCID: PMC3208506
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10138
CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis
Abstract
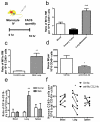
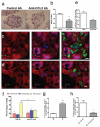
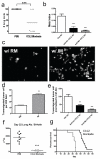
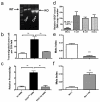
Macrophages, which are abundant in the tumour microenvironment, enhance malignancy. At metastatic sites, a distinct population of metastasis-associated macrophages promotes the extravasation, seeding and persistent growth of tumour cells. Here we define the origin of these macrophages by showing that Gr1-positive inflammatory monocytes are preferentially recruited to pulmonary metastases but not to primary mammary tumours in mice. This process also occurs for human inflammatory monocytes in pulmonary metastases of human breast cancer cells. The recruitment of these inflammatory monocytes, which express CCR2 (the receptor for chemokine CCL2), as well as the subsequent recruitment of metastasis-associated macrophages and their interaction with metastasizing tumour cells, is dependent on CCL2 synthesized by both the tumour and the stroma. Inhibition of CCL2-CCR2 signalling blocks the recruitment of inflammatory monocytes, inhibits metastasis in vivo and prolongs the survival of tumour-bearing mice. Depletion of tumour-cell-derived CCL2 also inhibits metastatic seeding. Inflammatory monocytes promote the extravasation of tumour cells in a process that requires monocyte-derived vascular endothelial growth factor. CCL2 expression and macrophage infiltration are correlated with poor prognosis and metastatic disease in human breast cancer. Our data provide the mechanistic link between these two clinical associations and indicate new therapeutic targets for treating metastatic breast cancer.
©2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cessation of CCL2 inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting angiogenesis.Nature. 2014 Nov 6;515(7525):130-3. doi: 10.1038/nature13862. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25337873
-
Chronic psychological stress promotes lung metastatic colonization of circulating breast cancer cells by decorating a pre-metastatic niche through activating β-adrenergic signaling.J Pathol. 2018 Jan;244(1):49-60. doi: 10.1002/path.4988. Epub 2017 Nov 15. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28940209
-
Targeting of tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma.Gut. 2017 Jan;66(1):157-167. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310514. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Gut. 2017. PMID: 26452628
-
Targeting the CCL2/CCR2 Axis in Cancer Immunotherapy: One Stone, Three Birds?Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 3;12:771210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.771210. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34804061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular structure and role of CCL2 (MCP-1) and C-C chemokine receptor CCR2 in skeletal biology and diseases.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Oct;236(10):7211-7222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30375. Epub 2021 Mar 30. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33782965 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of MDK as a Hypoxia- and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Related Gene Biomarker of Glioblastoma Based on a Novel Risk Model and In Vitro Experiments.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 1;12(1):92. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010092. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255198 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse Onco-Cardiology: What Is the Evidence for Breast Cancer? A Systematic Review of the Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 19;24(22):16500. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216500. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing monocytes after lung cancer surgery triggers the outgrowth of distant metastases, causing recurrence.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Sep 5;73(11):212. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03800-8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39235612 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance and targeting tumor-associated macrophages in cancer: new insights and future perspectives.Breast Cancer. 2021 May;28(3):539-555. doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01231-2. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33661479 Review.
-
Therapeutic Opportunities in Breast Cancer by Targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor as a Pleiotropic Cytokine.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Sep 6;18:11782234241276310. doi: 10.1177/11782234241276310. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 39246383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image Processing with Image. J. Biophotonics International. 2004;11:36–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

