GEBR-7b, a novel PDE4D selective inhibitor that improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses
- PMID: 21649644
- PMCID: PMC3246667
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01524.x
GEBR-7b, a novel PDE4D selective inhibitor that improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses
Abstract
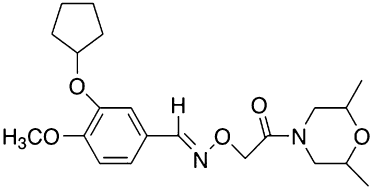
Background and purpose: Strategies designed to enhance cerebral cAMP have been proposed as symptomatic treatments to counteract cognitive deficits. However, pharmacological therapies aimed at reducing PDE4, the main class of cAMP catabolizing enzymes in the brain, produce severe emetic side effects. We have recently synthesized a 3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde derivative, structurally related to rolipram, and endowed with selective PDE4D inhibitory activity. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of the new drug, namely GEBR-7b, on memory performance, nausea, hippocampal cAMP and amyloid-β (Aβ) levels.
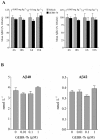
Experimental approach: To measure memory performance, we performed object recognition tests on rats and mice treated with GEBR-7b or rolipram. The emetic potential of the drug, again compared with rolipram, was evaluated in rats using the taste reactivity test and in mice using the xylazine/ketamine anaesthesia test. Extracellular hippocampal cAMP was evaluated by intracerebral microdialysis in freely moving rats. Levels of soluble Aβ peptides were measured in hippocampal tissues and cultured N2a cells by elisa.
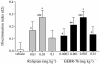
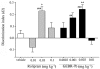
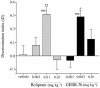
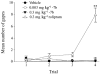
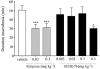
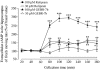
Key results: GEBR-7b increased hippocampal cAMP, did not influence Aβ levels and improved spatial, as well as object memory performance in the object recognition tests. The effect of GEBR-7b on memory was 3 to 10 times more potent than that of rolipram, and its effective doses had no effect on surrogate measures of emesis in rodents.
Conclusion and implications: Our results demonstrate that GEBR-7b enhances memory functions at doses that do not cause emesis-like behaviour in rodents, thus offering a promising pharmacological perspective for the treatment of memory impairment.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.015. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24067928
-
New insights into selective PDE4D inhibitors: 3-(Cyclopentyloxy)-4-methoxybenzaldehyde O-(2-(2,6-dimethylmorpholino)-2-oxoethyl) oxime (GEBR-7b) structural development and promising activities to restore memory impairment.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Nov 29;124:82-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.08.018. Epub 2016 Aug 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27560284
-
The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Apr 15;303:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.031. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26794595
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of new 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-4-methoxybenzaldehyde O-(2-(2,6-dimethylmorpholino)-2-oxoethyl) Oxime (GEBR-7b) related phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2014 Aug 28;57(16):7061-72. doi: 10.1021/jm500855w. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25126889
-
Proposal for pharmacologically distinct conformers of PDE4 cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases.Cell Signal. 1997 May-Jun;9(3-4):227-36. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(96)00173-8. Cell Signal. 1997. PMID: 9218122 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic therapy in Alzheimer's disease: a CREB-centric approach.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Jan;12(1):29-41. doi: 10.1007/s13311-014-0327-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 25575647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting LINC00152 activates cAMP/Ca2+/ferroptosis axis and overcomes tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):418. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06814-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38879508 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-induced phosphorylation of 26S proteasomes on Rpn6/PSMD11 enhances their activity and the degradation of misfolded proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 29;112(52):E7176-85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522332112. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26669444 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4D increases tau phosphorylation at Ser214 residue.Biofactors. 2022 Sep;48(5):1111-1117. doi: 10.1002/biof.1847. Epub 2022 May 13. Biofactors. 2022. PMID: 35561079 Free PMC article.
-
Male-Specific cAMP Signaling in the Hippocampus Controls Spatial Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Autism and Intellectual Disability.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 May 1;85(9):760-768. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.12.013. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30732858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruno O, Romussi A, Spallarossa A, Brullo C, Schenone S, Bondavalli F, et al. New selective phosphodiesterase 4D inhibitors differently acting on long, short, and supershort isoforms. J Med Chem. 2009;52:6546–6557. - PubMed
-
- Burgin AB, Magnusson OT, Singh J, Witte P, Staker BL, Bjornsson JM, et al. Design of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) allosteric modulators for enhancing cognition with improved safety. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:63–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

