Type XVII collagen regulates lamellipod stability, cell motility, and signaling to Rac1 by targeting bullous pemphigoid antigen 1e to alpha6beta4 integrin
- PMID: 21642434
- PMCID: PMC3143638
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.203646
Type XVII collagen regulates lamellipod stability, cell motility, and signaling to Rac1 by targeting bullous pemphigoid antigen 1e to alpha6beta4 integrin
Abstract
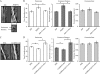
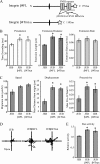
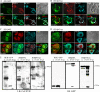
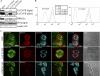
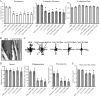
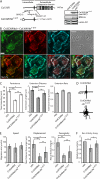
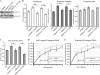
Rac1 activity, polarity, lamellipodial dynamics, and directed motility are defective in keratinocytes exhibiting deficiency in β4 integrin or knockdown of the plakin protein Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1e (BPAG1e). The activity of Rac, formation of stable lamellipodia, and directed migration are restored in β4 integrin-deficient cells by inducing expression of a truncated form of β4 integrin, which lacks binding sites for BPAG1e and plectin. In these same cells, BPAG1e, the truncated β4 integrin, and type XVII collagen (Col XVII), a transmembrane BPAG1e-binding protein, but not plectin, colocalize along the substratum-attached surface. This finding suggested to us that Col XVII mediates the association of BPAG1e and α6β4 integrin containing the truncated β4 subunit and supports directed migration. To test these possibilities, we knocked down Col XVII expression in keratinocytes expressing both full-length and truncated β4 integrin proteins. Col XVII-knockdown keratinocytes exhibit a loss in BPAG1e-α6β4 integrin interaction, a reduction in lamellipodial stability, an impairment in directional motility, and a decrease in Rac1 activity. These defects are rescued by a mutant Col XVII protein truncated at its carboxyl terminus. In summary, our results suggest that in motile cells Col XVII recruits BPAG1e to α6β4 integrin and is necessary for activation of signaling pathways, motile behavior, and lamellipodial stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BPAG1e maintains keratinocyte polarity through beta4 integrin-mediated modulation of Rac1 and cofilin activities.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jun;20(12):2954-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0051. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19403692 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane collagen XVII modulates integrin dependent keratinocyte migration via PI3K/Rac1 signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e87263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087263. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505282 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of the alpha6beta4 integrin in keratinocytes.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Nov;13(11):3845-58. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-01-0601. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12429829 Free PMC article.
-
Hemidesmosomal variants of epidermolysis bullosa. Mutations in the alpha6beta4 integrin and the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen/type XVII collagen genes.Exp Dermatol. 1998 Apr-Jun;7(2-3):46-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1998.tb00304.x. Exp Dermatol. 1998. PMID: 9583744 Review.
-
Molecular complexity of the cutaneous basement membrane zone.Mol Biol Rep. 1996;23(1):35-46. doi: 10.1007/BF00357071. Mol Biol Rep. 1996. PMID: 8983017 Review.
Cited by
-
Plakophilin 2 affects cell migration by modulating focal adhesion dynamics and integrin protein expression.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jan;134(1):112-122. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.266. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 23884246 Free PMC article.
-
BP180/Collagen XVII: A Molecular View.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(22):12233. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectraplakin family proteins - cytoskeletal crosslinkers with versatile roles.J Cell Sci. 2017 Aug 1;130(15):2447-2457. doi: 10.1242/jcs.196154. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28679697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the stem cell niche: role of collagen XVII in skin aging and wound repair.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 6;12(15):6446-6454. doi: 10.7150/thno.78016. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significant Role of Collagen XVII And Integrin β4 in Migration and Invasion of The Less Aggressive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 22;7:45057. doi: 10.1038/srep45057. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28327550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lauffenburger D. A., Horwitz A. F. (1996) Cell. 84, 359–369 - PubMed
-
- Hinz B., Alt W., Johnen C., Herzog V., Kaiser H. W. (1999) Exp. Cell Res. 251, 234–243 - PubMed
-
- Chodniewicz D., Klemke R. L. (2004) Exp. Cell Res. 301, 31–37 - PubMed
-
- Yang N., Higuchi O., Ohashi K., Nagata K., Wada A., Kangawa K., Nishida E., Mizuno K. (1998) Nature. 393, 809–812 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

