Molecular and cellular pharmacology of the novel noncamptothecin topoisomerase I inhibitor Genz-644282
- PMID: 21636699
- PMCID: PMC3155218
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1043
Molecular and cellular pharmacology of the novel noncamptothecin topoisomerase I inhibitor Genz-644282
Abstract
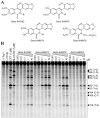
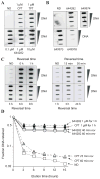
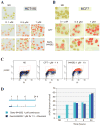
Camptothecin derivatives are powerful anticancer drugs because of their ability to trap topoisomerase I (Top1)-DNA cleavage complexes. However, they exhibit clinical limitations due to the instability of their α-hydroxylactone six-membered E-ring structure. In addition, they exhibit bone marrow and intestinal toxicity, especially in adults, and are drug efflux substrates. Here, we report a novel Top1 inhibitor, Genz-644282. We show that Genz-644282 and its metabolites induce Top1 cleavage at similar, as well as unique genomic positions, compared with camptothecin. The compound also induces protein-linked DNA breaks and Top1-DNA cleavage complexes that persist longer after compound removal than camptothecin. Concentration-dependent and persistent γH2AX formation was readily observed in cells treated with Genz-644282, and was present in greater than 50% of the cell population following 24 hours compound exposure. The compound shows partial cross-resistance in cell lines resistant to camptothecin. These cell lines include the human prostate DU145RC0.1 and the leukemic CEM/C2 cells. Limited cross-resistance to Genz-644282 was also found in the Top1 knockdown colon cancer (HCT116) and breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines and in human adenocarcinoma cells (KB31/KBV1) that overexpress (P-glycoprotein, ABCB1), a member of the ATP-binding cassette family of cell surface transport proteins known to confer MDR. Together, our results provide the first molecular and cellular characterization of Genz-644282 and its clinically relevant metabolites.
©2011 AACR
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of action of non-camptothecin inhibitor Genz-644282 in topoisomerase I inhibition.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 16;5(1):982. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03920-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36114357 Free PMC article.
-
New Topoisomerase I mutations are associated with resistance to camptothecin.Mol Cancer. 2011 May 27;10:64. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-64. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21619602 Free PMC article.
-
Novel indenoisoquinolines NSC 725776 and NSC 724998 produce persistent topoisomerase I cleavage complexes and overcome multidrug resistance.Cancer Res. 2007 Nov 1;67(21):10397-405. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0938. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17974983
-
Topoisomerase degradation, DSB repair, p53 and IAPs in cancer cell resistance to camptothecin-like topoisomerase I inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1835(1):11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23006513 Review.
-
Topoisomerase I inhibitors: Challenges, progress and the road ahead.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Jun 5;236:114304. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114304. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35413618 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of action of non-camptothecin inhibitor Genz-644282 in topoisomerase I inhibition.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 16;5(1):982. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03920-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36114357 Free PMC article.
-
DNA topoisomerases as molecular targets for anticancer drugs.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):1781-1799. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1821676. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32975138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects of Topoisomerase Inhibitors as Promising Anti-Cancer Agents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 13;16(10):1456. doi: 10.3390/ph16101456. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Widespread in vivo efficacy of The-0504: A conditionally-activatable nanoferritin for tumor-agnostic targeting of CD71-expressing cancers.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 6;9(10):e20770. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20770. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37860543 Free PMC article.
-
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids, berberine and coptisine, act against camptothecin-resistant topoisomerase I mutants.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):7718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87344-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33833336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Champoux JJ. DNA TOPOISOMERASES: Structure, Function, and Mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. A Journey in the World of DNA Rings and Beyond. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2009;78:31–54. - PubMed
-
- Teicher BA. Next generation topoisomerase I inhibitors: Rationale and biomarker strategies. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75:1262–71. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CJ, Rahier NJ, Hecht SM. Camptothecin: current perspectives. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004;12:1585–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

