Genetic editing of herpes simplex virus 1 and Epstein-Barr herpesvirus genomes by human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases in culture and in vivo
- PMID: 21632763
- PMCID: PMC3147940
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00290-11
Genetic editing of herpes simplex virus 1 and Epstein-Barr herpesvirus genomes by human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases in culture and in vivo
Abstract
Human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases target and edit single-stranded DNA, which can be of viral, mitochondrial, or nuclear origin. Retrovirus genomes, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) genomes deficient in the vif gene and the hepatitis B virus genome, are particularly vulnerable. The genomes of some DNA viruses, such as human papillomaviruses, can be edited in vivo and in transfection experiments. Accordingly, herpesviruses should be no exception. This is indeed the case for herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) in tissue culture, where APOBEC3C (A3C) overexpression can reduce virus titers and the particle/PFU ratio ∼10-fold. Nonetheless, A3A, A3G, and AICDA can edit what is presumably a small fraction of HSV genomes in an experimental setting without seriously impacting the viral titer. Hyperediting was found in HSV genomes recovered from 4/8 uncultured buccal lesions. The phenomenon is not restricted to HSV, since hyperedited Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genomes were readily recovered from 4/5 established cell lines, indicating that episomes are vulnerable to editing. These findings suggest that the widely expressed A3C cytidine deaminase can function as a restriction factor for some human herpesviruses. That the A3C gene is not induced by type I interferons begs the question whether some herpesviruses encode A3C antagonists.
Figures

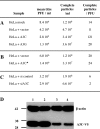
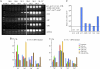
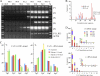

Similar articles
-
A Conserved Mechanism of APOBEC3 Relocalization by Herpesviral Ribonucleotide Reductase Large Subunits.J Virol. 2019 Nov 13;93(23):e01539-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01539-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31534038 Free PMC article.
-
Massive APOBEC3 editing of hepatitis B viral DNA in cirrhosis.PLoS Pathog. 2010 May 27;6(5):e1000928. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000928. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20523896 Free PMC article.
-
Host restriction of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 replication by human APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases but not murine APOBEC3.Virology. 2014 Apr;454-455:215-26. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.02.022. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24725948 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B: modern concepts in pathogenesis--APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases as effectors in innate immunity against the hepatitis B virus.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008 Jun;21(3):298-303. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3282fe1bb2. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18448976 Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 amplicons and their hybrid virus partners, EBV, AAV, and retrovirus.Curr Gene Ther. 2004 Dec;4(4):385-408. doi: 10.2174/1566523043346129. Curr Gene Ther. 2004. PMID: 15578989 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mechanism of APOBEC3B in Hepatitis B Virus Infection and HBV Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression, Therapeutic and Prognostic Potential.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Oct 17;17:4477-4486. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S484265. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39435460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synonymous nucleotide changes drive papillomavirus evolution.Tumour Virus Res. 2022 Dec;14:200248. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2022.200248. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Tumour Virus Res. 2022. PMID: 36265836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retroelements versus APOBEC3 family members: No great escape from the magnificent seven.Front Microbiol. 2012 Aug 14;3:275. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00275. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22912627 Free PMC article.
-
Human norovirus hyper-mutation revealed by ultra-deep sequencing.Infect Genet Evol. 2016 Jul;41:233-239. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 17. Infect Genet Evol. 2016. PMID: 27094861 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for host-dependent RNA editing in the transcriptome of SARS-CoV-2.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 17;6(25):eabb5813. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5813. eCollection 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32596474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beale R. C., et al. 2004. Comparison of the differential context-dependence of DNA deamination by APOBEC enzymes: correlation with mutation spectra in vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 337:585–596 - PubMed
-
- Bishop K. N., et al. 2004. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. 14:1392–1396 - PubMed
-
- Bonvin M., et al. 2006. Interferon-inducible expression of APOBEC3 editing enzymes in human hepatocytes and inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology 43:1364–1374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

