Host defense pathways: role of redundancy and compensation in infectious disease phenotypes
- PMID: 21616433
- PMCID: PMC3143490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.009
Host defense pathways: role of redundancy and compensation in infectious disease phenotypes
Abstract
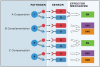
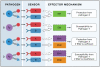
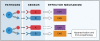
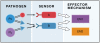
Innate host defense pathways consist of microbial sensors, their signaling pathways, and the antimicrobial effector mechanisms. Several classes of host defense pathways are currently known, each comprising several pattern-recognition receptors that detect different types of pathogens. These pathways interact with one another in a variety of ways that can be categorized into cooperation, complementation, and compensation. Understanding the principles of these interactions is important for better understanding of host defense mechanisms, as well as for correct interpretation of immunodeficient phenotypes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Microbial Infections Through Innate Immune Sensing of Nucleic Acids.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2018 Sep 8;72:447-478. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095605. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30200854 Review.
-
[The role of pattern-recognizing receptors in anti-infectious immunity].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2011;(10):47-54. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2011. PMID: 22168039 Review. Russian.
-
Activation of toll-like receptors by microbial lipoproteins: role in host defense.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001 Oct;108(4 Suppl):S104-6. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.118299. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11586275 Review.
-
Infectious diseases not immune to genome-wide association.Nat Genet. 2010 Sep;42(9):731-2. doi: 10.1038/ng0910-731. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20802473
-
Pneumonia models and innate immunity to respiratory bacterial pathogens.Shock. 2005 Dec;24 Suppl 1:12-8. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000191385.41689.f3. Shock. 2005. PMID: 16374367 Review.
Cited by
-
The Salmonella Effector Protein SopA Modulates Innate Immune Responses by Targeting TRIM E3 Ligase Family Members.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Apr 8;12(4):e1005552. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005552. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27058235 Free PMC article.
-
The DC receptor DNGR-1 mediates cross-priming of CTLs during vaccinia virus infection in mice.J Clin Invest. 2012 May;122(5):1628-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI60660. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22505455 Free PMC article.
-
Sensing adenovirus infection: activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 in RAW 264.7 cells.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(8):4527-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07071-11. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22345436 Free PMC article.
-
A Requirement for Argonaute 4 in Mammalian Antiviral Defense.Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 11;30(6):1690-1701.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.021. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32049003 Free PMC article.
-
A Modern-World View of Host-Microbiota-Pathogen Interactions.J Immunol. 2021 Oct 1;207(7):1710-1718. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100215. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34544813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arkwright PD, Abinun M, Cant AJ. Autoimmunity in human primary immunodeficiency diseases. Blood. 2002;99:2694–2702. - PubMed
-
- Elomaa O, Kangas M, Sahlberg C, Tuukkanen J, Sormunen R, Liakka A, Thesleff I, Kraal G, Tryggvason K. Cloning of a novel bacteria-binding receptor structurally related to scavenger receptors and expressed in a subset of macrophages. Cell. 1995;80:603–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

