Hierarchical regulation of mRNA partitioning between the cytoplasm and the endoplasmic reticulum of mammalian cells
- PMID: 21613539
- PMCID: PMC3135488
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0239
Hierarchical regulation of mRNA partitioning between the cytoplasm and the endoplasmic reticulum of mammalian cells
Abstract
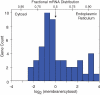
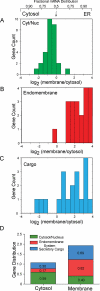
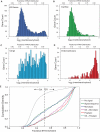
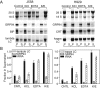
The mRNA transcriptome is currently thought to be partitioned between the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) compartments by binary selection; mRNAs encoding cytosolic/nucleoplasmic proteins are translated on free ribosomes, and mRNAs encoding topogenic signal-bearing proteins are translated on ER-bound ribosomes, with ER localization being conferred by the signal-recognition particle pathway. In subgenomic and genomic analyses of subcellular mRNA partitioning, we report an overlapping subcellular distribution of cytosolic/nucleoplasmic and topogenic signal-encoding mRNAs, with mRNAs of both cohorts displaying noncanonical subcellular partitioning patterns. Unexpectedly, the topogenic signal-encoding mRNA transcriptome was observed to partition in a hierarchical, cohort-specific manner. mRNAs encoding resident proteins of the endomembrane system were clustered at high ER-enrichment values, whereas mRNAs encoding secretory pathway cargo were broadly represented on free and ER-bound ribosomes. Two distinct modes of mRNA association with the ER were identified. mRNAs encoding endomembrane-resident proteins were bound via direct, ribosome-independent interactions, whereas mRNAs encoding secretory cargo displayed predominantly ribosome-dependent modes of ER association. These data indicate that mRNAs are partitioned between the cytosol and ER compartments via a hierarchical system of intrinsic and encoded topogenic signals and identify mRNA cohort-restricted modes of mRNA association with the ER.
Figures
Similar articles
-
De novo translation initiation on membrane-bound ribosomes as a mechanism for localization of cytosolic protein mRNAs to the endoplasmic reticulum.RNA. 2014 Oct;20(10):1489-98. doi: 10.1261/rna.045526.114. Epub 2014 Aug 20. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25142066 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of mRNA partitioning between the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum compartments of mammalian cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;419:197-214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-033-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369985
-
Stable ribosome binding to the endoplasmic reticulum enables compartment-specific regulation of mRNA translation.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Dec;16(12):5819-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-07-0685. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16221886 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways for compartmentalizing protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells: the template-partitioning model.Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;83(6):687-95. doi: 10.1139/o05-147. Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16333319 Review.
-
Take the (RN)A-train: localization of mRNA to the endoplasmic reticulum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1833(11):2519-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.01.013. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23353632 Review.
Cited by
-
p180 promotes the ribosome-independent localization of a subset of mRNA to the endoplasmic reticulum.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(5):e1001336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001336. Epub 2012 May 29. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 22679391 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular evidence that rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of calreticulin translation in Petunia pollen tubes growing in vitro.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Jul;34(7):1189-99. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1777-x. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25732863 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced gene expression results from selective mRNA partitioning to the endoplasmic reticulum.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 31;43(6):3219-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv167. Epub 2015 Mar 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25753659 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the protein-kinase mediated regulation of the HERG potassium channel synthesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1823(8):1273-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 May 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22613764 Free PMC article.
-
Live-cell mapping of organelle-associated RNAs via proximity biotinylation combined with protein-RNA crosslinking.Elife. 2017 Dec 14;6:e29224. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29224. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29239719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

