6-Bromoindirubin-3'-oxime inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells
- PMID: 21610112
- PMCID: PMC3107399
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3852
6-Bromoindirubin-3'-oxime inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells
Abstract
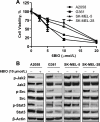
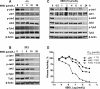
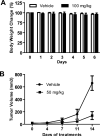
STAT3 is persistently activated and contributes to malignant progression in various cancers. Janus activated kinases (JAK) phosphorylate STAT3 in response to stimulation by cytokines or growth factors. The STAT3 signaling pathway has been validated as a promising target for development of anticancer therapeutics. Small-molecule inhibitors of JAK/STAT3 signaling represent potential molecular-targeted cancer therapeutic agents. In this study, we investigated the role of JAK/STAT3 signaling in 6-bromoindirubin-3'-oxime (6BIO)-mediated growth inhibition of human melanoma cells and assessed 6BIO as a potential anticancer drug candidate. We found that 6BIO is a pan-JAK inhibitor that induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells. 6BIO directly inhibited JAK-family kinase activity, both in vitro and in cancer cells. Apoptosis of human melanoma cells induced by 6BIO was associated with reduced phosphorylation of JAKs and STAT3 in both dose- and time-dependent manners. Consistent with inhibition of STAT3 signaling, expression of the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 was downregulated. In contrast to the decreased levels of phosphorylation of JAKs and STAT3, phosphorylation levels of the Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling proteins were not inhibited in cells treated with 6BIO. Importantly, 6BIO suppressed tumor growth in vivo with low toxicity in a mouse xenograft model of melanoma. Taken together, these results show that 6BIO is a novel pan-JAK inhibitor that can selectively inhibit STAT3 signaling and induces tumor cell apoptosis. Our findings support further development of 6BIO as a potential anticancer therapeutic agent that targets JAK/STAT3 signaling in tumor cells.
Figures
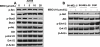

Similar articles
-
A novel 7-bromoindirubin with potent anticancer activity suppresses survival of human melanoma cells associated with inhibition of STAT3 and Akt signaling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Nov;13(13):1255-61. doi: 10.4161/cbt.21781. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22895078 Free PMC article.
-
MLS-2384, a new 6-bromoindirubin derivative with dual JAK/Src kinase inhibitory activity, suppresses growth of diverse cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 Feb;15(2):178-84. doi: 10.4161/cbt.26721. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24100507 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of Janus and Src family kinases by novel indirubin derivative blocks constitutively-activated Stat3 signaling associated with apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer cells.Mol Oncol. 2013 Jun;7(3):369-78. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23206899 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Apr;72(2):486-526. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018440. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32198236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of STAT3 in the initiation, progression, proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer and strategies to deliver JAK and STAT3 inhibitors.Life Sci. 2022 Nov 15;309:120996. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120996. Epub 2022 Sep 25. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36170890 Review.
Cited by
-
GSK3 inhibitors CHIR99021 and 6-bromoindirubin-3'-oxime inhibit microRNA maturation in mouse embryonic stem cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 2;5:8666. doi: 10.1038/srep08666. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25727520 Free PMC article.
-
AZD3759 inhibits glioma through the blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor and Janus kinase pathways.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8679-8689. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1991160. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34635007 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo animal models for studying brain metastasis: value and limitations.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013 Jun;30(5):695-710. doi: 10.1007/s10585-013-9566-9. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013. PMID: 23322381 Review.
-
Indirubin and Indirubin Derivatives for Counteracting Proliferative Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:654098. doi: 10.1155/2015/654098. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26457112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct On-Chip Differentiation of Intestinal Tubules from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 14;21(14):4964. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144964. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32674311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson DS, Horvath CM. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 2002;296:1653–5. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD. Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell. 2002;109(Suppl):S121–31. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE, Jr., Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264:1415–21. - PubMed
-
- Kisseleva T, Bhattacharya S, Braunstein J, Schindler CW. Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges. Gene. 2002;285:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

