Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA
- PMID: 21609964
- PMCID: PMC3167594
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr254
Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA
Abstract
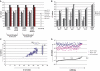
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of post-transcriptional gene expression regulators, have recently been detected in human body fluids, including peripheral blood plasma as extracellular nuclease resistant entities. However, the origin and function of extracellular circulating miRNA remain essentially unknown. Here, we confirmed that circulating mature miRNA in contrast to mRNA or snRNA is strikingly stable in blood plasma and cell culture media. Furthermore, we found that most miRNA in plasma and cell culture media completely passed through 0.22 µm filters but remained in the supernatant after ultracentrifugation at 110 000g indicating the non-vesicular origin of the extracellular miRNA. Furthermore, western blot immunoassay revealed that extracellular miRNA ultrafiltrated together with the 96 kDa Ago2 protein, a part of RNA-induced silencing complex. Moreover, miRNAs in both blood plasma and cell culture media co-immunoprecipited with anti-Ago2 antibody in a detergent free environment. This is the first study to show that extracellular miRNAs are predominantly exosomes/microvesicles free and are associated with Ago proteins. We hypothesize that extracellular miRNAs are in the most part by-products of dead cells that remain in extracellular space due to the high stability of the Ago2 protein and Ago2-miRNA complex. Nevertheless, our data does not reject the possibility that some miRNAs can be associated with exosomes.
Figures
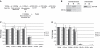

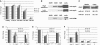
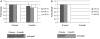
Comment in
-
Die hard: resilient RNAs in the blood.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jun;22(6):373. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00355-9. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33664511 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Extracellular microRNAs in human circulation are associated with miRISC complexes that are accessible to anti-AGO2 antibody and can bind target mimic oligonucleotides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 29;117(39):24213-24223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008323117. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32929008 Free PMC article.
-
Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 22;108(12):5003-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019055108. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21383194 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of circulating microRNA associated with RNA-binding protein.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1024:97-107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-453-1_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23719945
-
Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: An update on localization and biological role.Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Nov;51(3-4):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27396686 Review.
-
Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2016 Jun 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0536-0. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27343009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating microRNA signatures in mice exposed to lipoteichoic acid.J Biomed Sci. 2013 Jan 4;20(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-2. J Biomed Sci. 2013. PMID: 23286671 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Muscle-Specific miRNAs in Serum of Myotonic Dystrophy Patients Relate to Muscle Disease Progress.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 27;10(4):e0125341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125341. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25915631 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus-specific miRNAs and Argonaute2 play a role in the viral life cycle.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047490. Epub 2012 Oct 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23091627 Free PMC article.
-
Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 1;13:357. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-357. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22849433 Free PMC article.
-
Viral non-coding RNAs: Stealth strategies in the tug-of-war between humans and herpesviruses.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32631785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122:6–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev. Biol. 2006;289:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Hanke M, Hoefig K, Merz H, Feller AC, Kausch I, Jocham D, Warnecke JM, Sczakiel G. A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: microRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2009;28:655–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

