Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of KEAP1 disrupted and sulforaphane-treated human breast epithelial cells reveals common expression profiles
- PMID: 21597922
- PMCID: PMC3564494
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-011-1536-9
Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling of KEAP1 disrupted and sulforaphane-treated human breast epithelial cells reveals common expression profiles
Abstract
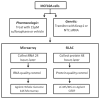
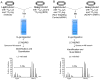
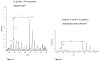
Sulforaphane (SFN), an isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables, is a potent inhibitor of experimental mammary carcinogenesis and may be an effective, safe chemopreventive agent for use in humans. SFN acts in part on the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway to regulate a battery of cytoprotective genes. In this study, transcriptomic and proteomic changes in the estrogen receptor negative, non-tumorigenic human breast epithelial MCF10A cell line were analyzed following SFN treatment or KEAP1 knockdown with siRNA using microarray and stable isotopic labeling with amino acids in culture (SILAC), respectively. Changes in selected transcripts and proteins were confirmed by PCR and Western blot in MCF10A and MCF12A cells. There was strong correlation between the transcriptomic and proteomic responses in both the SFN treatment (R = 0.679, P < 0.05) and KEAP1 knockdown (R = 0.853, P < 0.05) experiments. Common pathways for SFN treatment and KEAP1 knockdown were xenobiotic metabolism and antioxidants, glutathione metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism, and NADH/NADPH regeneration. Moreover, these pathways were most prominent in both the transcriptomic and the proteomic analyses. The aldo-keto reductase family members, AKR1B10, AKR1C1, AKR1C2 and AKR1C3, as well as NQO1 and ALDH3A1, were highly upregulated at both the transcriptomic and the proteomic levels. Collectively, these studies served to identify potential biomarkers that can be used in clinical trials to investigate the initial pharmacodynamic action of SFN in the breast.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
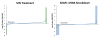




Similar articles
-
Reduced formation of depurinating estrogen-DNA adducts by sulforaphane or KEAP1 disruption in human mammary epithelial MCF-10A cells.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2587-92. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt246. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23843041 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 system by chemopreventive sulforaphane: implications of posttranslational modifications.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jul;1229:184-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06092.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21793854 Review.
-
Characterization of the cancer chemopreventive NRF2-dependent gene battery in human keratinocytes: demonstration that the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway, and not the BACH1-NRF2 pathway, controls cytoprotection against electrophiles as well as redox-cycling compounds.Carcinogenesis. 2009 Sep;30(9):1571-80. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp176. Epub 2009 Jul 16. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19608619 Free PMC article.
-
R-sulforaphane modulates the expression profile of AhR, ERα, Nrf2, NQO1, and GSTP in human breast cell lines.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Feb;476(2):525-533. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03913-5. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33064289 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprotection by sulforaphane: keep one eye beyond Keap1.Cancer Lett. 2006 Feb 28;233(2):208-18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.02.033. Cancer Lett. 2006. PMID: 16520150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging trends and hotspots of Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in nervous system diseases.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Nov 16;11(32):7833-7851. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i32.7833. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 38073678 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced 4-hydroxynonenal resistance in KEAP1 silenced human colon cancer cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:423965. doi: 10.1155/2013/423965. Epub 2013 May 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23766854 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin Is a Positive Regulator for Ferroptosis in Pancreatic Cancer.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Aug 5;18:457-466. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.002. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32953980 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of T cell metabolic reprogramming in cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2016 Dec;5(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0110-9. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27510264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Focus on Ferroptosis, Mitophagy and New Antioxidants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 12;11(4):769. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040769. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Nelson HD, Fu R, Griffin JC, Nygren P, Smith ME, Humphrey L. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness of medications to reduce risk for primary breast cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:703–715. W-226–735. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro TA, Fahey JW, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Stephenson KK, Wade KL, Ye L, Talalay P. Safety, tolerance, and metabolism of broccoli sprout glucosinolates and isothiocyanates: a clinical phase I study. Nutr Cancer. 2006;55:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Kensler TW, Chen JG, Egner PA, Fahey JW, Jacobson LP, Stephenson KK, Ye L, Coady JL, Wang JB, Wu Y, Sun Y, Zhang QN, Zhang BC, Zhu YR, Qian GS, Carmella SG, Hecht SS, Benning L, Gange SJ, Groopman JD, Talalay P. Effects of glucosinolate-rich broccoli sprouts on urinary levels of aflatoxin-DNA adducts and phenanthrene tetraols in a randomized clinical trial in He Zuo township, Qidong, People’s Republic of China. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14:2605–2613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

