Evaluation of ceftaroline activity versus daptomycin (DAP) against DAP-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model
- PMID: 21576449
- PMCID: PMC3122384
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00347-11
Evaluation of ceftaroline activity versus daptomycin (DAP) against DAP-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model
Abstract
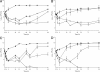
The objective of this study was to investigate the potential role of ceftaroline, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin, as a therapeutic option for the treatment of daptomycin-nonsusceptible (DNS) methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. Four clinical DNS MRSA strains, R5717, R5563, R5996 (heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus) and R5995 (vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus) were evaluated in a two-compartment hollow-fiber in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model at a starting inoculum of 10(7) CFU/ml for 96 h. Simulated regimens were ceftaroline at 600 mg every 12 h (q12h) (maximum free-drug concentration [fC(max)], 15.2 μg/ml; serum half-life [t(1/2)], 2.3 h), daptomycin at 6 mg/kg q24h (fC(max), 7.9 μg/ml; t(1/2), 8 h), and daptomycin at 10 mg/kg q24h (fC(max), 15.2 μg/ml; t(1/2), 8 h). Differences in CFU/ml between 24 and 96 h were evaluated by analysis of variance with Tukey's post-hoc test. Bactericidal activity was defined as a ≥3-log(10) CFU/ml decrease in the colony count from the initial inoculum. The ceftaroline MIC values were 0.25, 0.5, 0.5, and 0.5 μg/ml, and the daptomycin MIC values were 2, 2, 4, and 4 μg/ml for R5717, R5563, R5996, and R5995, respectively. Ceftaroline displayed sustained bactericidal activity against 3 of the 4 strains at 96 h (R5717, -3.1 log(10) CFU/ml; R5563, -2.5 log(10) CFU/ml; R5996, -5.77 log(10) CFU/ml; R5995, -6.38 log(10) CFU/ml). Regrowth occurred during the daptomycin at 6-mg/kg q24h regimen (4 strains) and the daptomycin at 10-mg/kg q24h regimen (3 strains). At 96 h, ceftaroline was significantly more active, resulting in CFU/ml counts lower than those obtained with daptomycin at 6 mg/kg q24h (4 strains, P ≤ 0.008) and daptomycin at 10 mg/kg q24 h (3 strains, P ≤ 0.001). Isolates with increased MIC values for daptomycin (all 4 strains) but not for ceftaroline were recovered. Ceftaroline was effective against the 4 isolates tested and may provide a clinical option for the treatment of DNS MRSA infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of ceftaroline, vancomycin, daptomycin, or ceftaroline plus daptomycin against daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jun;58(6):3177-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00088-14. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24663016 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Ceftaroline Alone and in Combination against Biofilm-Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Susceptibility to Daptomycin and Vancomycin in an In Vitro Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Aug;59(8):4497-503. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00386-15. Epub 2015 May 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25987623 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of telavancin activity versus daptomycin and vancomycin against daptomycin-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):955-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05849-11. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22123693 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical Impact of the Synergistic Mechanism of Daptomycin and Ceftaroline on Patients with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Infections.Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021;16(4):296-299. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666210108103813. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33423652 Review.
-
In vitro activity of ceftaroline against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae: a review of published studies and the AWARE Surveillance Program (2008-2010).Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Sep;55 Suppl 3:S206-14. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis563. Clin Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22903953 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of ceftaroline activity against heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-intermediate methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model: exploring the "seesaw effect".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jun;57(6):2664-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02308-12. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23545533 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Pneumonia with Ceftaroline Fosamil in a Patient with Inhalational Thermal Injury.Infect Dis Ther. 2015 Dec;4(4):519-28. doi: 10.1007/s40121-015-0096-4. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Infect Dis Ther. 2015. PMID: 26541469 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro pharmacodynamics of human simulated exposures of ceftaroline and daptomycin against MRSA, hVISA, and VISA with and without prior vancomycin exposure.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):672-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01516-13. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24217694 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of in vivo and in vitro pharmacodynamics of a humanized regimen of 600 milligrams of Ceftaroline Fosamil every 12 hours against Staphylococcus aureus at initial inocula of 106 and 108 CFU per milliliter.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Nov;58(11):6931-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03652-14. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 25136006 Free PMC article.
-
Addition of ceftaroline to daptomycin after emergence of daptomycin-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus during therapy improves antibacterial activity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Oct;56(10):5296-302. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00797-12. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22869564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andes D., Craig W. A. 2006. Pharmacodynamics of a new cephalosporin, PPI-0903 (TAK-599), active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in murine thigh and lung infection models: identification of an in vivo pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1376–1383 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boucher H. W., Sakoulas G. 2007. Perspectives on daptomycin resistance, with emphasis on resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 45:601–608 - PubMed
-
- Castanheira M., Jones R. N., Sader H. S. 2008. Update of the in vitro activity of daptomycin tested against 6710 Gram-positive cocci isolated in North America (2006). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 61:235–239 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically—eighth edition: approved standard M7–A8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical