Chondrocyte-specific microRNA-140 regulates endochondral bone development and targets Dnpep to modulate bone morphogenetic protein signaling
- PMID: 21576357
- PMCID: PMC3133397
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05178-11
Chondrocyte-specific microRNA-140 regulates endochondral bone development and targets Dnpep to modulate bone morphogenetic protein signaling
Abstract
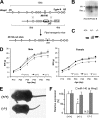
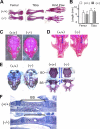
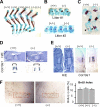
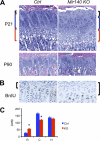
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in a variety of biological processes in diverse organisms, including mammals. In the mouse skeletal system, a global reduction of miRNAs in chondrocytes causes a lethal skeletal dysplasia. However, little is known about the physiological roles of individual miRNAs in chondrocytes. The miRNA-encoding gene, Mir140, is evolutionarily conserved among vertebrates and is abundantly and almost exclusively expressed in chondrocytes. In this paper, we show that loss of Mir140 in mice causes growth defects of endochondral bones, resulting in dwarfism and craniofacial deformities. Endochondral bone development is mildly advanced due to accelerated hypertrophic differentiation of chondrocytes in Mir140-null mice. Comparison of profiles of RNA associated with Argonaute 2 (Ago2) between wild-type and Mir140-null chondrocytes identified Dnpep as a Mir140 target. As expected, Dnpep expression was increased in Mir140-null chondrocytes. Dnpep overexpression showed a mild antagonistic effect on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling at a position downstream of Smad activation. Mir140-null chondrocytes showed lower-than-normal basal BMP signaling, which was reversed by Dnpep knockdown. These results demonstrate that Mir140 is essential for normal endochondral bone development and suggest that the reduced BMP signaling caused by Dnpep upregulation plays a causal role in the skeletal defects of Mir140-null mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of interleukin-10 in endochondral bone formation in mice: anabolic effect via the bone morphogenetic protein/Smad pathway.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Dec;65(12):3153-64. doi: 10.1002/art.38181. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 24022823
-
Reversing the miRNA -5p/-3p stoichiometry reveals physiological roles and targets of miR-140 miRNAs.RNA. 2022 Jun;28(6):854-864. doi: 10.1261/rna.079013.121. Epub 2022 Mar 24. RNA. 2022. PMID: 35332065 Free PMC article.
-
Rap1b Is an Effector of Axin2 Regulating Crosstalk of Signaling Pathways During Skeletal Development.J Bone Miner Res. 2017 Sep;32(9):1816-1828. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3171. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Bone Miner Res. 2017. PMID: 28520221 Free PMC article.
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
-
Integration of signaling pathways regulating chondrocyte differentiation during endochondral bone formation.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Dec;213(3):635-41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21262. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17886256 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone marrow stroma-derived miRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets of bone metastasis.Bonekey Rep. 2015 Apr 15;4:671. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2015.38. eCollection 2015. Bonekey Rep. 2015. PMID: 25908970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2 regulates skeletal growth by suppressing Wnt and TGF-β signalling.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 22;7:12047. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12047. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27329220 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs related to osteoporosis by high-throughput sequencing.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1451695. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451695. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39175544 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-140 promotes adipocyte lineage commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells via targeting osteopetrosis-associated transmembrane protein 1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8222-8230. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.426163. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23389033 Free PMC article.
-
High Fidelity of Mouse Models Mimicking Human Genetic Skeletal Disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Feb 4;10:934. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00934. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32117046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambros V., Chen X. 2007. The regulation of genes and genomes by small RNAs. Development 134:1635–1641 - PubMed
-
- Banegas I., et al. 2006. Brain aminopeptidases and hypertension. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 7:129–134 - PubMed
-
- Beitzinger M., Peters L., Zhu J. Y., Kremmer E., Meister G. 2007. Identification of human microRNA targets from isolated argonaute protein complexes. RNA Biol. 4:76–84 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
