Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome
- PMID: 21572440
- PMCID: PMC3571712
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1883
Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome
Abstract
Massively parallel sequencing of cDNA has enabled deep and efficient probing of transcriptomes. Current approaches for transcript reconstruction from such data often rely on aligning reads to a reference genome, and are thus unsuitable for samples with a partial or missing reference genome. Here we present the Trinity method for de novo assembly of full-length transcripts and evaluate it on samples from fission yeast, mouse and whitefly, whose reference genome is not yet available. By efficiently constructing and analyzing sets of de Bruijn graphs, Trinity fully reconstructs a large fraction of transcripts, including alternatively spliced isoforms and transcripts from recently duplicated genes. Compared with other de novo transcriptome assemblers, Trinity recovers more full-length transcripts across a broad range of expression levels, with a sensitivity similar to methods that rely on genome alignments. Our approach provides a unified solution for transcriptome reconstruction in any sample, especially in the absence of a reference genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
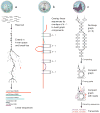
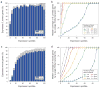
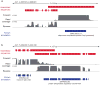

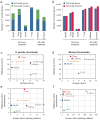
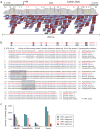
Comment in
-
RNA-Seq unleashed.Nat Biotechnol. 2011 Jul 11;29(7):599-600. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1915. Nat Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21747384 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis.Nat Protoc. 2013 Aug;8(8):1494-512. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.084. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23845962 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation transcriptome assembly.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Sep 7;12(10):671-82. doi: 10.1038/nrg3068. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21897427 Review.
-
Optimizing de novo transcriptome assembly from short-read RNA-Seq data: a comparative study.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Dec 14;12 Suppl 14(Suppl 14):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S14-S2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22373417 Free PMC article.
-
RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Aug 4;12:323. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21816040 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and annotating the genome using RNA-seq data.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Feb;60(2):116-125. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-0349-4. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27294835 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive analysis of the defense responses of Odontotermes formosanus (Shiraki) provides insights into the changes during Serratia marcescens infection.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 6;25(1):1044. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10955-2. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39506655
-
Tracing the evolutionary and genetic footprints of atmospheric tillandsioids transition from land to air.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):9599. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53756-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39505856
-
A chromosome-level genome assembly of a model conifer plant, the Japanese cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 5;25(1):1039. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10929-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39501145 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

