Class IIa histone deacetylases are hormone-activated regulators of FOXO and mammalian glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 21565617
- PMCID: PMC3117637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.043
Class IIa histone deacetylases are hormone-activated regulators of FOXO and mammalian glucose homeostasis
Abstract
Class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) are signal-dependent modulators of transcription with established roles in muscle differentiation and neuronal survival. We show here that in liver, class IIa HDACs (HDAC4, 5, and 7) are phosphorylated and excluded from the nucleus by AMPK family kinases. In response to the fasting hormone glucagon, class IIa HDACs are rapidly dephosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus where they associate with the promoters of gluconeogenic enzymes such as G6Pase. In turn, HDAC4/5 recruit HDAC3, which results in the acute transcriptional induction of these genes via deacetylation and activation of FOXO family transcription factors. Loss of class IIa HDACs in murine liver results in inhibition of FOXO target genes and lowers blood glucose, resulting in increased glycogen storage. Finally, suppression of class IIa HDACs in mouse models of type 2 diabetes ameliorates hyperglycemia, suggesting that inhibitors of class I/II HDACs may be potential therapeutics for metabolic syndrome.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
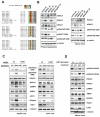
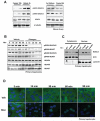
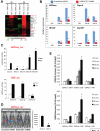
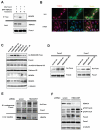
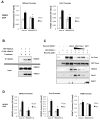
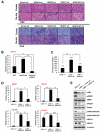
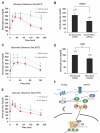
Comment in
-
Metabolic homeostasis: HDACs take center stage.Cell. 2011 May 13;145(4):497-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.017. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21565608 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic disease: New role for HDACs in glucose homeostasis.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Jul 1;10(7):492. doi: 10.1038/nrd3483. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21720402 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Metabolic Regulator Histone Deacetylase 9 Contributes to Glucose Homeostasis Abnormality Induced by Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Diabetes. 2015 Dec;64(12):4088-98. doi: 10.2337/db15-0197. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26420860
-
Liver-Specific Knockdown of Class IIa HDACs Has Limited Efficacy on Glucose Metabolism but Entails Severe Organ Side Effects in Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Aug 28;11:598. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00598. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32982982 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of Transcriptional Activity of Forkhead Box O1 by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Ameliorates Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 9;19(11):3539. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113539. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30424007 Free PMC article.
-
Class IIa HDACs - new insights into their functions in physiology and pathology.FEBS J. 2015 May;282(9):1736-44. doi: 10.1111/febs.13061. Epub 2014 Oct 27. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25244360 Review.
-
Regulatory signal transduction pathways for class IIa histone deacetylases.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;10(4):454-60. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 4. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20447866 Review.
Cited by
-
Lomitapide repurposing for treatment of malignancies: A promising direction.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 13;10(12):e32998. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32998. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38988566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIM3-AMPK-HDAC4/5 axis restricts MuERVL-marked 2-cell-like state in embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 Oct 11;17(10):2256-2271. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.08.009. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Stem Cell Reports. 2022. PMID: 36150380 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of CaMKK2 from the liver lowers blood glucose and improves whole-body glucose tolerance in the mouse.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Feb;26(2):281-91. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1299. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22240810 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of Hepatic Insulin Resistance.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 11;12:681356. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.681356. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34046015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycerol Monocaprylate Modulates Gut Microbiota and Increases Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production without Adverse Effects on Metabolism and Inflammation.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 23;13(5):1427. doi: 10.3390/nu13051427. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33922631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berdeaux R, Goebel N, Banaszynski L, Takemori H, Wandless T, Shelton GD, Montminy M. SIK1 is a class II HDAC kinase that promotes survival of skeletal myocytes. Nat Med. 2007;13:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Biddinger SB, Kahn CR. From mice to men: insights into the insulin resistance syndromes. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:123–158. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, et al. Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 2004;303:2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- Calnan DR, Brunet A. The FoxO code. Oncogene. 2008;27:2276–2288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD027183-18/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK062434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK062434-09S2/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080425-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049777/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD027183/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049777-17/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK083834/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD027183/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 DK062434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083834-25/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

