Gammadelta intraepithelial lymphocytes are essential mediators of host-microbial homeostasis at the intestinal mucosal surface
- PMID: 21555560
- PMCID: PMC3102410
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1019574108
Gammadelta intraepithelial lymphocytes are essential mediators of host-microbial homeostasis at the intestinal mucosal surface
Abstract
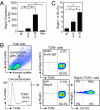
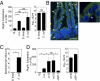
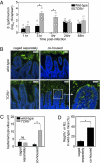
The mammalian gastrointestinal tract harbors thousands of bacterial species that include symbionts as well as potential pathogens. The immune responses that limit access of these bacteria to underlying tissue remain poorly defined. Here we show that γδ intraepithelial lymphocytes (γδ IEL) of the small intestine produce innate antimicrobial factors in response to resident bacterial "pathobionts" that penetrate the intestinal epithelium. γδ IEL activation was dependent on epithelial cell-intrinsic MyD88, suggesting that epithelial cells supply microbe-dependent cues to γδ IEL. Finally, γδ T cells protect against invasion of intestinal tissues by resident bacteria specifically during the first few hours after bacterial encounter, indicating that γδ IEL occupy a unique temporal niche among intestinal immune defenses. Thus, γδ IEL detect the presence of invading bacteria through cross-talk with neighboring epithelial cells and are an essential component of the hierarchy of immune defenses that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal interactions between commensal bacteria and gamma delta intraepithelial lymphocytes during mucosal injury.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 1;182(5):3047-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802705. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19234201 Free PMC article.
-
γδ Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Migration Limits Transepithelial Pathogen Invasion and Systemic Disease in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2015 Jun;148(7):1417-26. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.053. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25747597 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Characterization, and Culture of Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2121:141-152. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0338-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32147793
-
Three Layers of Intestinal γδ T Cells Talk Different Languages With the Microbiota.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:849954. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849954. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35422795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Microbiota and γδ T Cells: Insights into Immune Homeostasis and Neuro-Immune Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1747. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031747. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immunity in the small intestine.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;28(2):124-9. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3283506559. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22241076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal microbiota: shaping local and systemic immune responses.Semin Immunol. 2012 Feb;24(1):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2011.11.008. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Semin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22178452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the gut microbiota in the development and function of lymphoid cells.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1389-95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203100. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23378581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight Into the Intestinal Web of Mucosal Immunity, Microbiota, and Diet in Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 20;9:2617. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02617. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30532751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delayed gastrointestinal-associated lymphoid tissue reconstitution in duodenum compared with rectum in HIV-infected patients initiating antiretroviral therapy.AIDS. 2019 Dec 1;33(15):2289-2298. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002361. AIDS. 2019. PMID: 31764094 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Macpherson AJ, Uhr T. Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1662–1665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

