NPHP4, a cilia-associated protein, negatively regulates the Hippo pathway
- PMID: 21555462
- PMCID: PMC3166863
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201009069
NPHP4, a cilia-associated protein, negatively regulates the Hippo pathway
Abstract
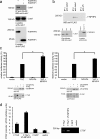
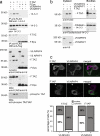
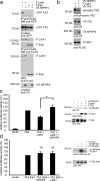
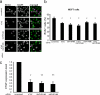
The conserved Hippo signaling pathway regulates organ size in Drosophila melanogaster and mammals and has an essential role in tumor suppression and the control of cell proliferation. Recent studies identified activators of Hippo signaling, but antagonists of the pathway have remained largely elusive. In this paper, we show that NPHP4, a known cilia-associated protein that is mutated in the severe degenerative renal disease nephronophthisis, acts as a potent negative regulator of mammalian Hippo signaling. NPHP4 directly interacted with the kinase Lats1 and inhibited Lats1-mediated phosphorylation of the Yes-associated protein (YAP) and TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding domain), leading to derepression of these protooncogenic transcriptional regulators. Moreover, NPHP4 induced release from 14-3-3 binding and nuclear translocation of YAP and TAZ, promoting TEA domain (TEAD)/TAZ/YAP-dependent transcriptional activity. Consistent with these data, knockdown of NPHP4 negatively affected cellular proliferation and TEAD/TAZ activity, essentially phenocopying loss of TAZ function. These data identify NPHP4 as a negative regulator of the Hippo pathway and suggest that NPHP4 regulates cell proliferation through its effects on Hippo signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Jul 28;19(8):996-1002. doi: 10.1038/ncb3581. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28752853 Free PMC article.
-
Vestigial-like family member 3 (VGLL3), a cofactor for TEAD transcription factors, promotes cancer cell proliferation by activating the Hippo pathway.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 26;295(26):8798-8807. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012781. Epub 2020 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32385107 Free PMC article.
-
The ciliopathy disease protein NPHP9 promotes nuclear delivery and activation of the oncogenic transcriptional regulator TAZ.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Dec 15;21(26):5528-38. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds408. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 23026745
-
Reciprocal regulation of YAP/TAZ by the Hippo pathway and the Small GTPase pathway.Small GTPases. 2020 Jul;11(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1435986. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29457552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippo pathway inhibition by blocking the YAP/TAZ-TEAD interface: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Dec;28(12):867-873. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1549226. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 30482112 Review.
Cited by
-
The ciliary protein nephrocystin-4 translocates the canonical Wnt regulator Jade-1 to the nucleus to negatively regulate β-catenin signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25370-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.385658. Epub 2012 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22654112 Free PMC article.
-
Cilia in cystic kidney and other diseases.Cell Signal. 2020 May;69:109519. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109519. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 31881326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transition zone proteins and cilia dynamics.Nat Genet. 2011 Jul 27;43(8):723-4. doi: 10.1038/ng.896. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21792235 No abstract available.
-
Regulation and functions of mammalian LATS/NDR kinases: looking beyond canonical Hippo signalling.Cell Biosci. 2013 Aug 28;3(1):32. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-3-32. Cell Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23985307 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling mediates proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic potential of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2014 Apr;7(2):309-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Transl Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24913676 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

