An HIV-1 gp120 envelope human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a C1 conformational epitope mediates potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity and defines a common ADCC epitope in human HIV-1 serum
- PMID: 21543485
- PMCID: PMC3126567
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00171-11
An HIV-1 gp120 envelope human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a C1 conformational epitope mediates potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity and defines a common ADCC epitope in human HIV-1 serum
Abstract
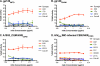
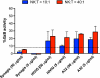
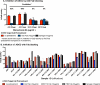
Among nonneutralizing HIV-1 envelope antibodies (Abs), those capable of mediating antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity have been postulated to be important for control of HIV-1 infection. ADCC-mediating Ab must recognize HIV-1 antigens expressed on the membrane of infected cells and bind the Fcγ receptor (FcR) of the effector cell population. However, the precise targets of serum ADCC antibody are poorly characterized. The human monoclonal antibody (MAb) A32 is a nonneutralizing antibody isolated from an HIV-1 chronically infected person. We investigated the ability of MAb A32 to recognize HIV-1 envelope expressed on the surface of CD4(+) T cells infected with primary and laboratory-adapted strains of HIV-1, as well as its ability to mediate ADCC activity. The MAb A32 epitope was expressed on the surface of HIV-1-infected CD4(+) T cells earlier than the CD4-inducible (CD4i) epitope bound by MAb 17b and the gp120 carbohydrate epitope bound by MAb 2G12. Importantly, MAb A32 was a potent mediator of ADCC activity. Finally, an A32 Fab fragment blocked the majority of ADCC-mediating Ab activity in plasma of subjects chronically infected with HIV-1. These data demonstrate that the epitope defined by MAb A32 is a major target on gp120 for plasma ADCC activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cocrystal Structures of Antibody N60-i3 and Antibody JR4 in Complex with gp120 Define More Cluster A Epitopes Involved in Effective Antibody-Dependent Effector Function against HIV-1.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):8840-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01232-15. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26085162 Free PMC article.
-
Structural definition of an antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity response implicated in reduced risk for HIV-1 infection.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12895-906. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02194-14. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25165110 Free PMC article.
-
Co-receptor Binding Site Antibodies Enable CD4-Mimetics to Expose Conserved Anti-cluster A ADCC Epitopes on HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins.EBioMedicine. 2016 Oct;12:208-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 9. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27633463 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope specificity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity [ADCC] responses.Curr HIV Res. 2013 Jul;11(5):378-87. doi: 10.2174/1570162x113116660059. Curr HIV Res. 2013. PMID: 24191939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Basis for Epitopes in the gp120 Cluster A Region that Invokes Potent Effector Cell Activity.Viruses. 2019 Jan 16;11(1):69. doi: 10.3390/v11010069. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30654465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Display Potential for Prevention of HIV-1 Infection of Mucosal Tissue Superior to That of Nonneutralizing Antibodies.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01762-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01762-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795431 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein conformation to decrease the HIV-1 reservoir.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Jun 9;29(6):904-916.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.04.014. Epub 2021 May 20. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 34019804 Free PMC article.
-
A novel assay for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against HIV-1- or SIV-infected cells reveals incomplete overlap with antibodies measured by neutralization and binding assays.J Virol. 2012 Nov;86(22):12039-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01650-12. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22933282 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity-Competent Antibodies against HIV-1-Infected Cells in Plasma from HIV-Infected Subjects.mBio. 2019 Dec 17;10(6):e02690-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02690-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31848282 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the interplay between NK cells and HIV: therapeutic implications.J Leukoc Biol. 2023 Feb 1;113(2):109-138. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiac007. J Leukoc Biol. 2023. PMID: 36822173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baum L. L., et al. 1996. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J. Immunol. 157:2168–2173 - PubMed
-
- Chung A., Rollman E., Johansson S., Kent S. J., Stratov I. 2008. The utility of ADCC responses in HIV infection. Curr. HIV Res. 6:515–519 - PubMed
-
- Chung A. W., Rollman E., Center R. J., Kent S. J., Stratov I. 2009. Rapid degranulation of NK cells following activation by HIV-specific antibodies. J. Immunol. 182:1202–1210 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

