Interpretation of fluctuation spectra in lipid bilayer simulations
- PMID: 21539777
- PMCID: PMC3149257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.03.010
Interpretation of fluctuation spectra in lipid bilayer simulations
Abstract
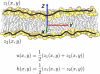
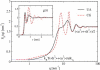
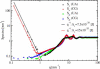
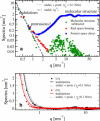
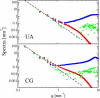
Atomic resolution and coarse-grained simulations of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine lipid bilayers were analyzed for fluctuations perpendicular to the bilayer using a completely Fourier-based method. We find that the fluctuation spectrum of motions perpendicular to the bilayer can be decomposed into just two parts: 1), a pure undulation spectrum proportional to q(-4) that dominates in the small-q regime; and 2), a molecular density structure factor contribution that dominates in the large-q regime. There is no need for a term proportional to q(-2) that has been postulated for protrusion fluctuations and that appeared to have been necessary to fit the spectrum for intermediate q. We suggest that earlier reports of such a term were due to the artifact of binning and smoothing in real space before obtaining the Fourier spectrum. The observability of an intermediate protrusion regime from the fluctuation spectrum is discussed based on measured and calculated material constants.
Copyright © 2011 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Testing procedures for extracting fluctuation spectra from lipid bilayer simulations.J Chem Phys. 2014 Aug 14;141(6):064114. doi: 10.1063/1.4892422. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 25134558 Free PMC article.
-
A consistent model for thermal fluctuations and protein-induced deformations in lipid bilayers.Biophys J. 2006 Mar 1;90(5):1501-20. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.075838. Epub 2005 Dec 2. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16326916 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion and spectroscopy of water and lipids in fully hydrated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes.J Chem Phys. 2014 Mar 14;140(10):104901. doi: 10.1063/1.4867385. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 24628199
-
Interpretation of Phase Boundary Fluctuation Spectra in Biological Membranes with Nanoscale Organization.J Chem Theory Comput. 2020 Apr 14;16(4):2736-2750. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.9b00929. Epub 2020 Mar 20. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020. PMID: 32125851
-
Coarse-grained simulation: a high-throughput computational approach to membrane proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Feb;36(Pt 1):27-32. doi: 10.1042/BST0360027. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18208379 Review.
Cited by
-
SMARTINI3 parametrization of multi-scale membrane models via unsupervised learning methods.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75490-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468134 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Machine Learning to Greatly Expand the Range and Accuracy of Bottom-Up Coarse-Grained Models through Virtual Particles.J Chem Theory Comput. 2023 Jul 25;19(14):4402-4413. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.2c01183. Epub 2023 Feb 20. J Chem Theory Comput. 2023. PMID: 36802592 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid clustering correlates with membrane curvature as revealed by molecular simulations of complex lipid bilayers.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Oct 23;10(10):e1003911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003911. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25340788 Free PMC article.
-
Electron videography of a lipid-protein tango.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 19;10(16):eadk0217. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk0217. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38630809 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Domain Co-localization Induced by Membrane Undulations.Biophys J. 2017 Feb 28;112(4):655-662. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.12.030. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28256225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans E., Rawicz W. Entropy-driven tension and bending elasticity in condensed-fluid membranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990;64:2094–2097. - PubMed
-
- Evans E. Entropy-driven tension in vesicle membranes and unbinding of adherent vesicles. Langmuir. 1991;7:1900–1908.
-
- König S., Pfeiffer W., Sackmann E.E. Molecular dynamics of lipid bilayers studied by incoherent quasi-elastic neutron scattering. J. Phys. II (France) 1992;2:1589–1615.
-
- König S., Sackmann E. Molecular and collective dynamics of lipid bilayers. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996;1:78–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

