Overexpression of a chromatin remodeling factor, RSF-1/HBXAP, correlates with aggressive oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 21514451
- PMCID: PMC3081206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.01.043
Overexpression of a chromatin remodeling factor, RSF-1/HBXAP, correlates with aggressive oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
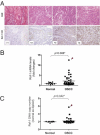
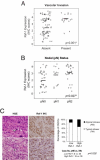
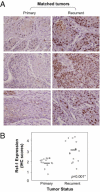
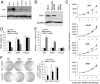
RSF-1, also known as hepatitis B X-antigen associated protein (HBXAP), is a subunit of an ISWI chromatin remodeling complex, remodeling and spacing factor (RSF). Recent studies have provided new evidence that chromatin remodeling participates in the pathogenesis of neoplastic diseases by altering cell cycle regulation and gene expression. In this report, we studied the biological roles of RSF-1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), a highly invasive neoplastic disease. Based on IHC and quantitative real-time PCR, we demonstrated that RSF-1 expression could be detected in the majority of OSCC cases, and the levels were significantly higher in OSCC cells than in their normal counterparts. Moreover, expression levels of RSF-1 significantly correlated with the presence of angiolymphatic invasion, abnormal mitoses, metastasis, tumor recurrence, and advanced stage disease at presentation. Univariate and multivariate analyses showed a significant association of RSF-1 overexpression and worse overall survival in OSCC patients. RSF-1 knockdown remarkably decreased cellular proliferation and induced apoptosis in OSCC cells with high RSF-1 expression levels, but not in those without. Taken together, our results suggest that RSF-1 up-regulation is associated with several clinicopathological features of disease aggressiveness in OSCC patients, and RSF-1 plays an important role in maintaining cellular growth and survival in OSCC.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rsf-1/HBXAP overexpression is independent of gene amplification and is associated with poor outcome in patients with urinary bladder urothelial carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2012 Sep;65(9):802-7. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200897. Epub 2012 Jun 9. J Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22685262
-
Overexpression of Rsf-1 correlates with pathological type, p53 status and survival in primary breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5595-608. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337201 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010 Oct;110(4):484-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.04.009. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. PMID: 20868995
-
Associations of Rsf-1 overexpression with poor therapeutic response and worse survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2012 Mar;65(3):248-53. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2011-200413. Epub 2011 Nov 12. J Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22081787
-
Collagen Triple Helix Repeat Containing-1 (CTHRC1) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Prognostic Value and Clinico-Pathological Implications.Int J Med Sci. 2015 Nov 1;12(12):937-45. doi: 10.7150/ijms.11605. eCollection 2015. Int J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664254 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rsf-1 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis and cell proliferation in colon cancer.Tumour Biol. 2012 Oct;33(5):1485-91. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0399-y. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22528946
-
RSF1 is a positive regulator of NF-κB-induced gene expression required for ovarian cancer chemoresistance.Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 15;74(8):2258-69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2459. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24566868 Free PMC article.
-
High RSF-1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(7):668-73. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22977663 Free PMC article.
-
Oral squamous cell carcinomas: state of the field and emerging directions.Int J Oral Sci. 2023 Sep 22;15(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00249-w. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 37736748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARID1A, a factor that promotes formation of SWI/SNF-mediated chromatin remodeling, is a tumor suppressor in gynecologic cancers.Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 1;71(21):6718-27. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1562. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21900401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Workman J.L., Kingston R.E. Alteration of nucleosome structure as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:545–579. - PubMed
-
- Wolffe A.P. Chromatin remodeling: why it is important in cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:2988–2990. - PubMed
-
- Lafon-Hughes L., Di Tomaso M.V., Mendez-Acuna L., Martinez-Lopez W. Chromatin-remodelling mechanisms in cancer. Mutat Res. 2008;658:191–214. - PubMed
-
- Wiegand K.C., Shah S.P., Al-Agha O.M., Zhao Y., Tse K., Zeng T., Senz J., McConechy M., Anglesio M.S., Kalloger S.E., Yang W., Heravi-Moussavi A., Giuliany R., Chow C., Fee J., Zayed A., Melnyk N., Turashvili G., Delaney A., Madore J., Yip S., McPherson A.W., Ha G., Bell L., Fereday S., Tam A., Galletta L., Tonin P.N., Provencher D., Miller D., Jones S., Moore R.A., Morin G.B., Oloumi A., Boyd N., Aparicio S.A., Shih I.M., Mes-Masson A., Bowtell D., Hirst M., Gilks B., Marra M.A., Huntsman D.G. ARID1A gene mutations in endometriosis associated ovarian carcinomas. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1532–1543. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

