Rhinovirus-induced barrier dysfunction in polarized airway epithelial cells is mediated by NADPH oxidase 1
- PMID: 21507984
- PMCID: PMC3126521
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02074-10
Rhinovirus-induced barrier dysfunction in polarized airway epithelial cells is mediated by NADPH oxidase 1
Abstract
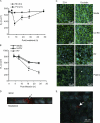
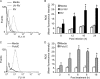
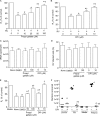
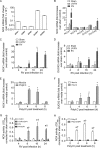
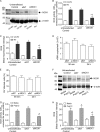
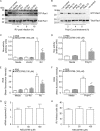
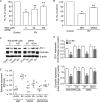
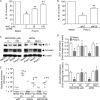
Previously, we showed that rhinovirus (RV), which is responsible for the majority of common colds, disrupts airway epithelial barrier function, as evidenced by reduced transepithelial resistance (R(T)), dissociation of zona occludins 1 (ZO-1) from the tight junction complex, and bacterial transmigration across polarized cells. We also showed that RV replication is required for barrier function disruption. However, the underlying biochemical mechanisms are not known. In the present study, we found that a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) mimetic, poly(I:C), induced tight junction breakdown and facilitated bacterial transmigration across polarized airway epithelial cells, similar to the case with RV. We also found that RV and poly(I:C) each stimulated Rac1 activation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and Rac1-dependent NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) activity. Inhibitors of Rac1 (NSC23766), NOX (diphenylene iodonium), and NOX1 (small interfering RNA [siRNA]) each blocked the disruptive effects of RV and poly(I:C) on R(T), as well as the dissociation of ZO-1 and occludin from the tight junction complex. Finally, we found that Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) is not required for either poly(I:C)- or RV-induced reductions in R(T). Based on these results, we concluded that Rac1-dependent NOX1 activity is required for RV- or poly(I:C)-induced ROS generation, which in turn disrupts the barrier function of polarized airway epithelia. Furthermore, these data suggest that dsRNA generated during RV replication is sufficient to disrupt barrier function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nod-like receptor X-1 is required for rhinovirus-induced barrier dysfunction in airway epithelial cells.J Virol. 2014 Apr;88(7):3705-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03039-13. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24429360 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinovirus disrupts the barrier function of polarized airway epithelial cells.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Dec 15;178(12):1271-81. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200801-136OC. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18787220 Free PMC article.
-
ROS Is Involved in Disruption of Tight Junctions of Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Induced by HRV16.Laryngoscope. 2018 Dec;128(12):E393-E401. doi: 10.1002/lary.27510. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Laryngoscope. 2018. PMID: 30325507
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 modulates cytokine induction from toll like receptor activated, but not rhinovirus infected, primary human airway smooth muscle.Respir Res. 2013 Nov 15;14(1):127. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-127. Respir Res. 2013. PMID: 24237854 Free PMC article.
-
H. influenzae potentiates airway epithelial cell responses to rhinovirus by increasing ICAM-1 and TLR3 expression.FASEB J. 2006 Oct;20(12):2121-3. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-5806fje. Epub 2006 Aug 16. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16914605
Cited by
-
Aberrantly activated EGFR contributes to enhanced IL-8 expression in COPD airways epithelial cells via regulation of nuclear FoxO3A.Thorax. 2013 Feb;68(2):131-41. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-201719. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Thorax. 2013. PMID: 23099361 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis, gasdermins and allergic diseases.Allergy. 2024 Sep;79(9):2380-2395. doi: 10.1111/all.16236. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39003568 Review.
-
TLR2 Activation Limits Rhinovirus-Stimulated CXCL-10 by Attenuating IRAK-1-Dependent IL-33 Receptor Signaling in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Sep 15;197(6):2409-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502702. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27503209 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus infection: mechanisms of redox control and novel therapeutic opportunities.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jan 10;18(2):186-217. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4307. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22799599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway epithelial CD47 plays a critical role in inducing influenza virus-mediated bacterial super-infection.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 30;15(1):3666. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47963-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38693120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedard K., Krause K. H. 2007. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 87:245–313 - PubMed
-
- Berube J., Bourdon C., Yao Y., Rousseau S. 2009. Distinct intracellular signaling pathways control the synthesis of IL-8 and RANTES in TLR1/TLR2, TLR3 or NOD1 activated human airway epithelial cells. Cell. Signal. 21:448–456 - PubMed
-
- Biagioli M. C., Kaul P., Singh I., Turner R. B. 1999. The role of oxidative stress in rhinovirus induced elaboration of IL-8 by respiratory epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26:454–462 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

