Allostery in a disordered protein: oxidative modifications to α-synuclein act distally to regulate membrane binding
- PMID: 21491910
- PMCID: PMC3110780
- DOI: 10.1021/ja2009554
Allostery in a disordered protein: oxidative modifications to α-synuclein act distally to regulate membrane binding
Abstract
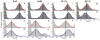
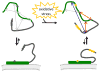
Both oxidative stress and aggregation of the protein α-synuclein (aS) have been implicated as key factors in the etiology of Parkinson's disease. Specifically, oxidative modifications to aS disrupt its binding to lipid membranes, an interaction considered critical to its native function. Here we seek to provide a mechanistic explanation for this phenomenon by investigating the effects of oxidative nitration of tyrosine residues on the structure of aS and its interaction with lipid membranes. Membrane binding is mediated by the first ∼95 residues of aS. We find that nitration of the single tyrosine (Y39) in this domain disrupts binding due to electrostatic repulsion. Moreover, we observe that nitration of the three tyrosines (Y125/133/136) in the C-terminal domain is equally effective in perturbing binding, an intriguing result given that the C-terminus is not thought to interact directly with the lipid bilayer. Our investigations show that tyrosine nitration results in a change of the conformational states populated by aS in solution, with the most prominent changes occurring in the C-terminal region. These results lead us to suggest that nitration of Y125/133/136 reduces the membrane-binding affinity of aS through allosteric coupling by altering the ensemble of conformational states and depopulating those capable of membrane binding. While allostery is a well-established concept for structured proteins, it has only recently been discussed in the context of disordered proteins. We propose that allosteric regulation through modification of specific residues in, or ligand binding to, the C-terminus may even be a general mechanism for modulating aS function.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures
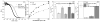
Similar articles
-
Elucidating the Role of Site-Specific Nitration of α-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease via Protein Semisynthesis and Mutagenesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Apr 22;137(15):5041-52. doi: 10.1021/ja5131726. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25768729
-
Phosphorylation of α-Synuclein at Y125 and S129 alters its metal binding properties: implications for understanding the role of α-Synuclein in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease and related disorders.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Nov 16;2(11):667-75. doi: 10.1021/cn200074d. Epub 2011 Sep 14. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22860160 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of post-translational modifications in regulating α-synuclein interactions by studying the effects of phosphorylation on nanobody binding.Protein Sci. 2018 Jul;27(7):1262-1274. doi: 10.1002/pro.3412. Protein Sci. 2018. PMID: 29603451 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lipids Interacting with α-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7(3):433-450. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171103. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017. PMID: 28671142 Review.
-
Nitration in neurodegeneration: deciphering the "Hows" "nYs".Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 26;46(25):7325-36. doi: 10.1021/bi700430y. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17542619 Review.
Cited by
-
αSynuclein and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pathogenic Partnership in Parkinson's Disease?Parkinsons Dis. 2012;2012:829207. doi: 10.1155/2012/829207. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Parkinsons Dis. 2012. PMID: 22737587 Free PMC article.
-
Role of post-translational modifications on the alpha-synuclein aggregation-related pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.BMB Rep. 2022 Jul;55(7):323-335. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.7.073. BMB Rep. 2022. PMID: 35733294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-Specific Three-Color Labeling of α-Synuclein via Conjugation to Uniquely Reactive Cysteines during Assembly by Native Chemical Ligation.Cell Chem Biol. 2018 Jun 21;25(6):797-801.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Cell Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29681525 Free PMC article.
-
Shedding light on protein folding, structural and functional dynamics by single molecule studies.Molecules. 2014 Nov 25;19(12):19407-34. doi: 10.3390/molecules191219407. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25429564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the Interactions Between α-Synuclein and Lipid Membranes by Post-translational Modifications.Front Neurol. 2021 Jul 15;12:661117. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.661117. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34335440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:164–173. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, et al. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Singleton AB, et al. Science. 2003;302:841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

