Nutrigenetic disruption of inflammation-resolution homeostasis and atherogenesis
- PMID: 21474962
- PMCID: PMC3080581
- DOI: 10.1159/000326890
Nutrigenetic disruption of inflammation-resolution homeostasis and atherogenesis
Abstract
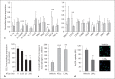
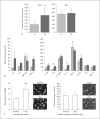
Background/aim: Pro-resolving and anti-inflammatory mediator products of murine 12/15-lipoxygenase (LOX) exhibit potent actions on vascular inflammation and protect against the progression of atherosclerosis. The present study was designed to determine whether augmenting dietary lipids modulates the body's endogenous anti-inflammatory pro-resolving mechanisms and promotes atherosclerosis.
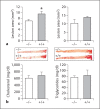
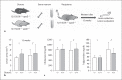
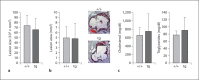
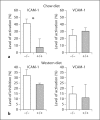
Methods/results: We investigated the biometabolic consequences of variations in lipid mediator biosynthesis using genetic knockout and overexpression models of 12/15-LOX mice fed the commonly used 'Western diet'. Unexpectedly, this high-fat diet annulled the protective actions of 12/15-LOX, and the combination of a Western diet and 12/15-LOX overexpression paradoxically promoted inflammation leading to production of diet-related and 12/15-LOX-dependent blood mediators that differentially activated endothelial cells via expression of ICAM-1. Hyperlipidemia not only affected the biosynthesis of lipoxin A4, a key pro-resolving mediator, but also disrupted the protective pro-resolving function of 12/15-LOX products, and the enzyme pathway no longer protected against atherosclerosis in vivo.
Conclusion: We uncovered a novel mechanism whereby a high-fat diet as well as hyperlipidemia disrupt the homeostasis of inflammation resolution. These findings underscore the importance of dietary essential PUFAs and LOX-derived lipid mediators in combination with lipid-lowering agents in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage beta3 integrin suppresses hyperlipidemia-induced inflammation by modulating TNFalpha expression.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Dec;27(12):2699-706. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.153650. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951320
-
I4, a synthetic anti-diabetes agent, attenuates atherosclerosis through its lipid-lowering, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis properties.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Jan 15;440:80-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27725191
-
IGF-1 reduces inflammatory responses, suppresses oxidative stress, and decreases atherosclerosis progression in ApoE-deficient mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Dec;27(12):2684-90. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.156257. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17916769
-
Inhibitors of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway in atherosclerosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(27):3116-32. doi: 10.2174/138161209789058020. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19754386 Review.
-
The two faces of the 15-lipoxygenase in atherosclerosis.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2007 Aug;77(2):67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2007. PMID: 17869078 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Inflammation-Resolution Provide Clues to Treat Patients According to Their Plaque Phenotype?Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 7;10:205. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00205. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30899222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage Trafficking, Inflammatory Resolution, and Genomics in Atherosclerosis: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 2).J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Oct 30;72(18):2181-2197. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2147. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30360827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
12/15-Lipoxygenase signaling in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar 15;302(6):E654-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00373.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22215650 Free PMC article.
-
12- and 15-lipoxygenases in adipose tissue inflammation.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013 Jul-Aug;104-105:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013. PMID: 22951339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inverse Association between Omega-3 Index and Severity of COVID-19: A Case-Control Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 25;19(11):6445. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116445. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Chiang N, Arita M, Serhan CN. Anti-inflammatory circuitry: lipoxin, aspirin-triggered lipoxins and their receptor ALX. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005;73:163–177. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN. Lipoxin biosynthesis and its impact in inflammatory and vascular events. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1212:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin biosynthesis: an update and role in anti-inflammation and pro-resolution. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002;68–69:433–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

