Toll-like receptor 3 signaling enables human esophageal epithelial cells to sense endogenous danger signals released by necrotic cells
- PMID: 21474651
- PMCID: PMC3129934
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00471.2010
Toll-like receptor 3 signaling enables human esophageal epithelial cells to sense endogenous danger signals released by necrotic cells
Abstract
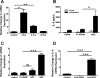
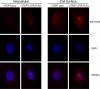
The mechanisms by which gastroesophageal reflux disease esophagitis develops are controversial. Although many support the notion that caustic injury leads to reflux esophagitis, others have proposed that reflux esophagitis is caused by esophageal epithelial cytokine-mediated inflammation. We previously demonstrated that Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) is highly expressed and functional in the nontransformed human esophageal epithelial cell line EPC2-hTERT. In addition to activation by viral double-stranded RNA, TLR3 can be activated by endogenous mRNA released by necrotic cells. In the present study, we investigated the role of esophageal epithelial TLR3 to sense danger signals released by necrotic esophageal epithelial cells in vitro. Following induction of freeze-thaw necrosis, necrotic EPC2-hTERT cell supernatants (NCS) were used to stimulate EPC2-hTERT monolayers, leading to NF-κB-dependent induction of IL-8 mRNA expression. Responses to self-derived NCS were not observed in transformed gastrointestinal epithelial cell lines, including TE-1 and Caco-2 cells, suggesting that the ability to sense endogenous danger signals is unique to nontransformed esophageal epithelial cells. To determine the immunostimulatory role of epithelial RNA, EPC2-hTERT cells were stimulated with self-derived mRNA, which significantly induced IL-8 mRNA expression. Finally, suppression of TLR3 signaling in a DN-TLR3 cell line, hTERT-ΔTIR-TLR3, led to reduced NCS-induced IL-8 induction by both NCS and mRNA stimulation. Our results demonstrate that human esophageal epithelial cells can sense endogenous danger signals, in part through TLR3 signaling. This supports the concept that epithelial injury plays an inciting role in the pathogenesis of reflux-induced esophagitis, providing important insights into the mechanisms by which epithelial injury leads to inflammation.
Figures
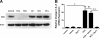
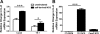


Similar articles
-
TLR3-mediated NF-{kappa}B signaling in human esophageal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):G1172-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00065.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19779021 Free PMC article.
-
Necrosis-induced TLR3 Activation Promotes TLR2 Expression in Gingival Cells.J Dent Res. 2015 Aug;94(8):1149-57. doi: 10.1177/0022034515589289. Epub 2015 Jun 4. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 26045329
-
Preferential Secretion of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) by Terminally Differentiated Esophageal Epithelial Cells: Relevance to Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE).PLoS One. 2016 Mar 18;11(3):e0150968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150968. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26992000 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathways: pathogenesis and clinical implications of microbiome alteration in esophagitis and Barrett esophagus.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 15;18(8):2138-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0934. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22344232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reflux esophagitis and its role in the pathogenesis of Barrett's metaplasia.J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jul;52(7):767-776. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1342-1. Epub 2017 Apr 27. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28451845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibition by simvastatin of IRF3 phosphorylation and TSLP production in dsRNA-challenged bronchial epithelial cells from COPD donors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;168(2):363-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02131.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22881993 Free PMC article.
-
Human esophageal myofibroblasts secrete proinflammatory cytokines in response to acid and Toll-like receptor 4 ligands.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Jun 1;308(11):G904-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00333.2014. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25882613 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinovirus and dsRNA induce RIG-I-like receptors and expression of interferon β and λ1 in human bronchial smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 29;8(4):e62718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062718. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658644 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2 stimulation augments esophageal barrier integrity.Allergy. 2019 Dec;74(12):2449-2460. doi: 10.1111/all.13968. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31267532 Free PMC article.
-
TLR3 Expression is a Potential Prognosis Biomarker and Shapes the Immune-Active Tumor Microenvironment in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 28;15:1437-1456. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S348786. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35250293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey K. Cutting edge: HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165: 2950–2954, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Aimanianda V, Haensler J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Novel cellular and molecular mechanisms of induction of immune responses by aluminum adjuvants. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30: 287–295, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Andl CD, Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Oyama K, Harada H, Chruma K, Herlyn M, Rustgi AK. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 278: 1824–1830, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Binder RJ, Suto R, Anderson KM, Srivastava PK. Necrotic but not apoptotic cell death releases heat shock proteins, which deliver a partial maturation signal to dendritic cells and activate the NF-κB pathway. Int Immunol 12: 1539–1546, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

