Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulates neutrophil chemotactic responses in inflammatory arthritis in mice
- PMID: 21452319
- PMCID: PMC3069137
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30203
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulates neutrophil chemotactic responses in inflammatory arthritis in mice
Abstract
Objective: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) facilitates multiple aspects of inflammatory arthritis, the pathogenesis of which has been significantly linked to the activity of neutrophils. The effects of MIF on neutrophil recruitment are unknown. This study was undertaken to investigate the contribution of MIF to the regulation of neutrophil chemotactic responses.
Methods: K/BxN serum-transfer arthritis was induced in wild-type (WT), MIF(-/-) , and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1; CCL2)-deficient mice as well as in WT mice treated with monoclonal antibodies to cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (anti-KC). Leukocyte trafficking in vivo was examined using intravital microscopy, and neutrophil function in vitro was examined using migration chambers and assessment of MAP kinase activation.
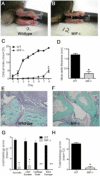
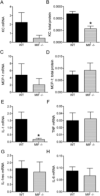
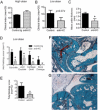
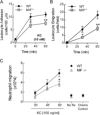
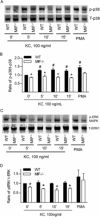
Results: K/BxN serum-transfer arthritis was markedly attenuated in MIF(-/-) mice, with reductions in the clinical and histologic severity of arthritis and the synovial expression of KC and interleukin-1. Arthritis was also reduced by anti-KC antibody treatment, but not in MCP-1-deficient mice. In vivo, neutrophil recruitment responses to KC were reduced in MIF(-/-) mice. Similarly, MIF(-/-) mouse neutrophils exhibited reduced chemotactic responses to KC in vitro, despite displaying unaltered chemokine receptor expression. Reduced chemotactic responses of MIF(-/-) mouse neutrophils were associated with reduced phosphorylation of p38 and ERK MAP kinases.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that MIF promotes neutrophil trafficking in inflammatory arthritis via facilitation of chemokine-induced migratory responses and MAP kinase activation. Therapeutic MIF inhibition could limit synovial neutrophil recruitment.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and CD74 regulate macrophage chemotactic responses via MAPK and Rho GTPase.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 15;186(8):4915-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003713. Epub 2011 Mar 16. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21411731 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-derived, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is necessary to induce disease in the K/BxN serum-induced model of arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Sep;33(9):2301-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2713-4. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23503937 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced arthritis in MIF deficient mice is associated with reduced T cell activation: down-regulation of ERK MAP kinase phosphorylation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 May;152(2):372-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03639.x. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18341611 Free PMC article.
-
The role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the inflammatory immune response and rheumatoid arthritis.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2006 Jan;156(1-2):11-8. doi: 10.1007/s10354-005-0243-8. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 16465610 Review.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:12-22. doi: 10.2741/1501. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15576336 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Targeting of a Disease-Related Conformational Isoform of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Ameliorates Inflammatory Conditions.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):2343-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500572. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26209628 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for decreased induction of class IB PI3-kinases expression by MIF inhibitors.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jan;21(1):142-153. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12949. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27619729 Free PMC article.
-
TRPP2 dysfunction decreases ATP-evoked calcium, induces cell aggregation and stimulates proliferation in T lymphocytes.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Sep 13;20(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1540-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31514750 Free PMC article.
-
Leishmania-encoded orthologs of macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulate host immunity to promote parasite persistence.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2249-65. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500189R. Epub 2016 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26956417 Free PMC article.
-
New aspects of RpoE in uropathogenic Proteus mirabilis.Infect Immun. 2015 Mar;83(3):966-77. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02232-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25547796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Shah MR, Hosaka S, Halloran MM, Haines GK, et al. Growth-related gene product alpha. A chemotactic cytokine for neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1995;155(7):3660–6. - PubMed
-
- Eyles JL, Hickey MJ, Norman MU, Croker BA, Roberts AW, Drake SF, et al. A key role for G-CSF-induced neutrophil production and trafficking during inflammatory arthritis. Blood. 2008;112(13):5193–201. - PubMed
-
- Brown CR, Blaho VA, Loiacono CM. Susceptibility to experimental Lyme arthritis correlates with KC and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production in joints and requires neutrophil recruitment via CXCR2. J. Immunol. 2003;171(2):893–901. - PubMed
-
- Verri WA, Jr., Souto FO, Vieira SM, Almeida SC, Fukada SY, Xu D, et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 May 14; (Epub ahead of print) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

