A MEK inhibitor abrogates myeloproliferative disease in Kras mutant mice
- PMID: 21451123
- PMCID: PMC3265440
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001069
A MEK inhibitor abrogates myeloproliferative disease in Kras mutant mice
Abstract
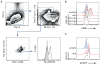
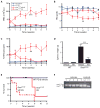
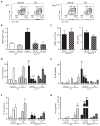
Chronic and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemias (CMML and JMML) are aggressive myeloproliferative neoplasms that are incurable with conventional chemotherapy. Mutations that deregulate Ras signaling play a central pathogenic role in both disorders, and Mx1-Cre, Kras(LSL-G12D) mice that express the Kras oncogene develop a fatal disease that closely mimics these two leukemias in humans. Activated Ras controls multiple downstream effectors, but the specific pathways that mediate the leukemogenic effects of hyperactive Ras are unknown. We used PD0325901, a highly selective pharmacological inhibitor of mitogen-activated or extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase (MEK), a downstream component of the Ras signaling network, to address how deregulated Raf/MEK/ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) signaling drives neoplasia in Mx1-Cre, Kras(LSL-G12D) mice. PD0325901 treatment induced a rapid and sustained reduction in leukocyte counts, enhanced erythropoiesis, prolonged mouse survival, and corrected the aberrant proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow progenitor cells. These responses were due to direct effects of PD0325901 on Kras mutant cells rather than to stimulation of normal hematopoietic cell proliferation. Consistent with the in vivo response, inhibition of MEK reversed the cytokine hypersensitivity characteristic of Kras(G12D) hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Our data demonstrate that deregulated Raf/MEK/ERK signaling is integral to the growth of Kras-mediated myeloproliferative neoplasms and further suggest that MEK inhibition could be a useful way to ameliorate functional hematologic abnormalities in patients with CMML and JMML.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
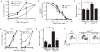
Similar articles
-
MEK inhibition exhibits efficacy in human and mouse neurofibromatosis tumors.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jan;123(1):340-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI60578. Epub 2012 Dec 10. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23221341 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth.Nature. 2010 Mar 18;464(7287):431-5. doi: 10.1038/nature08833. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20130576
-
Combined MEK and JAK inhibition abrogates murine myeloproliferative neoplasm.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jun;124(6):2762-73. doi: 10.1172/JCI74182. Epub 2014 May 8. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24812670 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to MEK inhibitors: should we co-target upstream?Sci Signal. 2011 Mar 29;4(166):pe16. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001948. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21447797 Review.
-
The role of mitogen-activated ERK-kinase inhibitors in lung cancer therapy.Clin Lung Cancer. 2005 Nov;7(3):221-3. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2005.n.040. Clin Lung Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16354319 Review.
Cited by
-
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia: molecular pathogenesis informs current approaches to therapy and hematopoietic cell transplantation.Front Pediatr. 2014 Mar 28;2:25. doi: 10.3389/fped.2014.00025. eCollection 2014. Front Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24734223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data for the MEK1/2 inhibitor pimasertib in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies.Blood Cancer J. 2015 Dec 11;5(12):e375. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.103. Blood Cancer J. 2015. PMID: 26657199 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Mechanistic and Preclinical Insights from Mouse Models of Hematologic Cancer Characterized by Hyperactive Ras.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018 Apr 2;8(4):a031526. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031526. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018. PMID: 28778967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Criteria for evaluating response and outcome in clinical trials for children with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia.Haematologica. 2015 Jan;100(1):17-22. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.109892. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 25552679 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of MEK inhibition in acute myelogenous leukemia: rationale for "vertical" and "lateral" combination strategies.J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Oct;90(10):1133-44. doi: 10.1007/s00109-012-0886-z. Epub 2012 Mar 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22399013
References
-
- Emanuel PD. Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2008;22:1335–1342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA084221/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA84221/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08CA103868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA103868-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08CA119105/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA72614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA072614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA128583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA119105-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA084221-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA072614-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA103868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA128583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA119105/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

