Angiotensin II type 1 receptor signalling regulates microRNA differentially in cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes
- PMID: 21449976
- PMCID: PMC3174419
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01375.x
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor signalling regulates microRNA differentially in cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes
Abstract
Background and purpose: The angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT(1)R) is a key regulator of blood pressure and cardiac contractility and is profoundly involved in development of cardiac disease. Since several microRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated in cardiac disease, we determined whether miRNAs might be regulated by AT(1)R signals in a Gαq/11-dependent or -independent manner.
Experimental approach: We performed a global miRNA array analysis of angiotensin II (Ang II)-mediated miRNA regulation in HEK293N cells overexpressing the AT(1)R and focused on separating the role of Gαq/11-dependent and -independent pathways. MiRNA regulation was verified with quantitative PCR in both HEK293N cells and primary cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts.
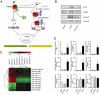
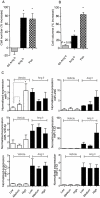
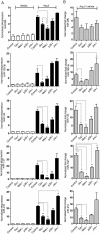
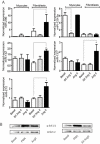
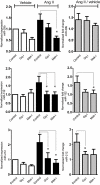
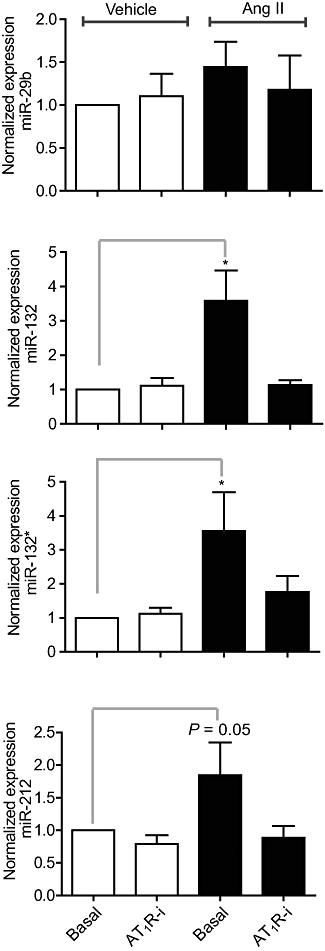
Key results: Our studies revealed five miRNAs (miR-29b, -129-3p, -132, -132* and -212) that were up-regulated by Ang II in HEK293N cells. In contrast, the biased Ang II analogue, [Sar1, Ile4, Ile8] Ang II (SII Ang II), which selectively activates Gαq/11-independent signalling, failed to regulate miRNAs in HEK293N cells. Furthermore, Ang II-induced miRNA regulation was blocked following Gαq/11 and Mek1 inhibition. The observed Ang II regulation of miRNA was confirmed in primary cultures of adult cardiac fibroblasts. Interestingly, Ang II did not regulate miRNA expression in cardiac myocytes, but SII Ang II significantly down-regulated miR-129-3p.
Conclusions and implications: Five miRNAs were regulated by Ang II through mechanisms depending on Gαq/11 and Erk1/2 activation. These miRNAs may be involved in Ang II-mediated cardiac biology and disease, as several of these miRNAs have previously been associated with cardiovascular disease and were found to be regulated in cardiac cells.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
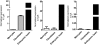
Similar articles
-
AT(1) receptor Gαq protein-independent signalling transcriptionally activates only a few genes directly, but robustly potentiates gene regulation from the β2-adrenergic receptor.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Jan 1;331(1):49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 20708651
-
Angiotensin II confers resistance to apoptosis in cardiac myofibroblasts through the AT1/ERK1/2/RSK1 pathway.IUBMB Life. 2019 Feb;71(2):261-276. doi: 10.1002/iub.1967. Epub 2018 Nov 19. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 30452117
-
[Sar1, Ile4, Ile8]-angiotensin II Potentiates Insulin Receptor Signalling and Glycogen Synthesis in Hepatocytes.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 May;122(5):460-469. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12937. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29136335
-
Cell type-specific angiotensin II-evoked signal transduction pathways: critical roles of Gbetagamma subunit, Src family, and Ras in cardiac fibroblasts.Circ Res. 1998 Feb 23;82(3):337-45. doi: 10.1161/01.res.82.3.337. Circ Res. 1998. PMID: 9486662 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-204 regulates type 1 IP3R to control vascular smooth muscle cell contractility and blood pressure.Cell Calcium. 2019 Jun;80:18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 30925290 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA in Endothelial Dysfunction and Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016 Dec;18(12):87. doi: 10.1007/s11906-016-0696-8. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016. PMID: 27837398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in miR-132-Based Biomarker and Therapeutic Potential in the Cardiovascular System.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 2;12:751487. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.751487. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34795586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: potential regulators of renal development genes that contribute to CAKUT.Pediatr Nephrol. 2014 Apr;29(4):565-74. doi: 10.1007/s00467-013-2599-0. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 23996519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System-Mediated Cardiovascular Inflammation and Remodeling.Int J Inflam. 2015;2015:101527. doi: 10.1155/2015/101527. Epub 2015 May 6. Int J Inflam. 2015. PMID: 26064773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Wei H, Lefkowitz RJ. Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35518–35525. - PubMed
-
- Akishita M, Iwai M, Wu L, Zhang L, Ouchi Y, Dzau VJ, et al. Inhibitory effect of angiotensin II type 2 receptor on coronary arterial remodeling after aortic banding in mice. Circulation. 2000;102:1684–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

