Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis
- PMID: 21445232
- PMCID: PMC3060165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017745
Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains one of the major cancer types and cancer related death worldwide. Sensitive, non-invasive biomarkers that can facilitate disease detection, staging and prediction of therapeutic outcome are highly desirable to improve survival rate and help to determine optimized treatment for CRC. The small non-coding RNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs), have recently been identified as critical regulators for various diseases including cancer and may represent a novel class of cancer biomarkers. The purpose of this study was to identify and validate circulating microRNAs in human plasma for use as such biomarkers in colon cancer.
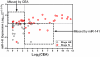
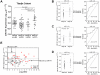
Methodology/principal findings: By using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, we found that circulating miR-141 was significantly associated with stage IV colon cancer in a cohort of 102 plasma samples. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of candidate plasma microRNA markers. We observed that combination of miR-141 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a widely used marker for CRC, further improved the accuracy of detection. These findings were validated in an independent cohort of 156 plasma samples collected at Tianjin, China. Furthermore, our analysis showed that high levels of plasma miR-141 predicted poor survival in both cohorts and that miR-141 was an independent prognostic factor for advanced colon cancer.
Conclusions/significance: We propose that plasma miR-141 may represent a novel biomarker that complements CEA in detecting colon cancer with distant metastasis and that high levels of miR-141 in plasma were associated with poor prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


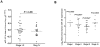
Similar articles
-
Plasma miR-183 predicts recurrence and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(2):268-75. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1002327. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25629978 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating exosomal miR-125a-3p as a novel biomarker for early-stage colon cancer.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 23;7(1):4150. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04386-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28646161 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer: circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers.Oncol Rep. 2013 Jul;30(1):320-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2475. Epub 2013 May 15. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23673725
-
Exosome-Encapsulated microRNAs as Potential Circulating Biomarkers in Colon Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1705-1709. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161201144634. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27908272 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of colon cancer.Dig Dis. 2012;30 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):9-15. doi: 10.1159/000341882. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Dig Dis. 2012. PMID: 23207927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: The State of Play.Prostate Cancer. 2013;2013:539680. doi: 10.1155/2013/539680. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Prostate Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23577261 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs in serum: novel biomarkers for patients with bladder cancer?World J Urol. 2014 Apr;32(2):353-8. doi: 10.1007/s00345-012-1010-2. Epub 2012 Dec 25. World J Urol. 2014. PMID: 23266581
-
An elevated serum miR-141 level in patients with bone-metastatic prostate cancer is correlated with more bone lesions.Asian J Androl. 2013 Mar;15(2):231-5. doi: 10.1038/aja.2012.116. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Asian J Androl. 2013. PMID: 23377530 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MACC1 transcripts in colorectal cancer patient plasma predict metastasis and prognosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049249. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166620 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of microRNA-34a expression profile and rs2666433 variant in colorectal cancer: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 9;10(1):16940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73951-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33037254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alwan A. World Health Organization. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2007;1:7–8. - PubMed
-
- Hegde SR, Sun W, Lynch JP. Systemic and targeted therapy for advanced colon cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2:135–149. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Fakih MG, Padmanabhan A. CEA monitoring in colorectal cancer. What you should know. Oncology (Williston Park) 2006;20:579–587; discussion 588, 594, 596 passim. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

