Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells
- PMID: 21439085
- PMCID: PMC3072949
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-108
Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Exosomes consist of membrane vesicles that are secreted by several cell types, including tumors and have been found in biological fluids. Exosomes interact with other cells and may serve as vehicles for the transfer of protein and RNA among cells.
Methods: SKOV3 exosomes were labelled with carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl-ester and collected by ultracentrifugation. Uptake of these vesicles, under different conditions, by the same cells from where they originated was monitored by immunofluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry analysis. Lectin analysis was performed to investigate the glycosylation properties of proteins from exosomes and cellular extracts.
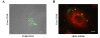
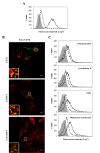
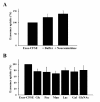
Results: In this work, the ovarian carcinoma SKOV3 cell line has been shown to internalize exosomes from the same cells via several endocytic pathways that were strongly inhibited at 4°C, indicating their energy dependence. Partial colocalization with the endosome marker EEA1 and inhibition by chlorpromazine suggested the involvement of clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Furthermore, uptake inhibition in the presence of 5-ethyl-N-isopropyl amiloride, cytochalasin D and methyl-beta-cyclodextrin suggested the involvement of additional endocytic pathways. The uptake required proteins from the exosomes and from the cells since it was inhibited after proteinase K treatments. The exosomes were found to be enriched in specific mannose- and sialic acid-containing glycoproteins. Sialic acid removal caused a small but non-significant increase in uptake. Furthermore, the monosaccharides D-galactose, α-L-fucose, α-D-mannose, D-N-acetylglucosamine and the disaccharide β-lactose reduced exosomes uptake to a comparable extent as the control D-glucose.
Conclusions: In conclusion, exosomes are internalized by ovarian tumor cells via various endocytic pathways and proteins from exosomes and cells are required for uptake. On the other hand, exosomes are enriched in specific glycoproteins that may constitute exosome markers. This work contributes to the knowledge about the properties and dynamics of exosomes in cancer.
Figures


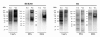
Similar articles
-
Exosomes Promote Ovarian Cancer Cell Invasion through Transfer of CD44 to Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Jan;15(1):78-92. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0191. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27758876
-
Exosomes in the ascites of ovarian cancer patients: origin and effects on anti-tumor immunity.Oncol Rep. 2011 Mar;25(3):749-62. doi: 10.3892/or.2010.1119. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21181093
-
In-depth proteomic analyses of ovarian cancer cell line exosomes reveals differential enrichment of functional categories compared to the NCI 60 proteome.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Mar 21;445(4):694-701. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.070. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24434149
-
The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of exosomes in epithelial ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 May 15;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0659-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28506269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internalization of Exosomes through Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis.Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Feb;17(2):337-347. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0891. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Mol Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30487244 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Post-Translational Modifications in Targeting Protein Cargo to Extracellular Vesicles.Subcell Biochem. 2021;97:45-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_3. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33779913
-
Glycoproteomic Analysis of Human Urinary Exosomes.Anal Chem. 2020 Nov 3;92(21):14357-14365. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01952. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32985870 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation by dietary microRNAs.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;93(12):1097-102. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0392. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26222444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Innocent Bystanders or Critical Culprits in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 13;9:635104. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.635104. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34055771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvesicles derived from dermal myofibroblasts modify the integrity of the blood and lymphatic barriers using distinct endocytosis pathways.J Extracell Biol. 2024 May 2;3(5):e151. doi: 10.1002/jex2.151. eCollection 2024 May. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38939570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denzer K, Kleijmeer MJ, Heijnen HF, Stoorvogel W, Geuze HJ. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(19):3365–3374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

