Interaction of mutant hepatitis B X protein with p53 tumor suppressor protein affects both transcription and cell survival
- PMID: 21438026
- PMCID: PMC3125428
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20767
Interaction of mutant hepatitis B X protein with p53 tumor suppressor protein affects both transcription and cell survival
Abstract
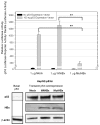
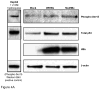
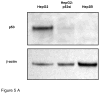
This study examines the differential activities between wild-type Hepatitis B virus X protein (WtHBx) and a mutant HBx (MutHBx), which bears a hotspot mutation at nucleotides 1,762 and 1,764, resulting in a lysine to methionine change at codon 130 and a valine to isoleucine change at codon 131. This mutation leads to hepatocellular carcinoma, and we evaluated how WtHBx and MutHBx proteins differ in their interactions with the p53 tumor suppressor protein. This was experimentally addressed through co-immunoprecipitation assays examining the interaction between WtHBx and MutHBx proteins with p53, reporter assays determining the impact of the HBx proteins on p53-mediated gene transcription, and clonogenic survival assays evaluating the effect of HBx on cell growth in lines of varying p53-expression status. Both WtHBx and MutHBx proteins physically interact with p53 protein, but have different impacts on p53-mediated gene transcription. WtHBx did not effect p53-mediated gene transcription, whereas MutHBx inhibited it (P < 0.01). MutHBx inhibited colony formation in p53-proficient cells (P < 0.01), but not p53-deficient lines. Although both HBx proteins interact with p53, they affect p53-mediated gene transcription differently. WtHBx has no effect, whereas MutHBx inhibits it. In clonogenic survival assays, MutHBx inhibited cell growth in p53-proficient cells rather than enhanced it. This suggests that for MutHBx to behave oncogenically, the p53 pathway must be crippled or absent. This study has identified some important novel ways in which WtHBx and MutHBx differentially interact with p53 and this could begin to form the cellular explanation for the association between this particular mutant and liver cancer.
Copyright ©2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits nucleotide excision repair.Int J Cancer. 1999 Mar 15;80(6):875-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990315)80:6<875::aid-ijc13>3.0.co;2-z. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10074921
-
Inhibition of hepatitis-B-virus core promoter by p53: implications for carcinogenesis in hepatocytes.Int J Cancer. 1996 Sep 17;67(6):892-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960917)67:6<892::AID-IJC21>3.0.CO;2-2. Int J Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8824564
-
Altered binding site selection of p53 transcription cassettes by hepatitis B virus X protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;33(3):485-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01189-12. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23149944 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jan;26 Suppl 1:144-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06546.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21199526 Review.
-
Hepatocarcinogenesis in viral Hepatitis B infection: the role of HBx and p53.Acta Med Indones. 2006 Jul-Sep;38(3):154-9. Acta Med Indones. 2006. PMID: 16953033 Review.
Cited by
-
TP53 R249S mutation, genetic variations in HBX and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in The Gambia.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Jun;33(6):1219-24. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs068. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22759751 Free PMC article.
-
The Hepatitis B Virus Interactome: A Comprehensive Overview.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 16;12:724877. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.724877. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34603251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus molecular biology and pathogenesis.Hepatoma Res. 2016;2:163-186. doi: 10.20517/2394-5079.2016.05. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Hepatoma Res. 2016. PMID: 28042609 Free PMC article.
-
Interference of Apoptosis by Hepatitis B Virus.Viruses. 2017 Aug 18;9(8):230. doi: 10.3390/v9080230. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28820498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population attributable risk of aflatoxin-related liver cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Cancer. 2012 Sep;48(14):2125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Eur J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22405700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garcia M, Jemal A, Ward E, Center M, Hao Y, Siegel R, Thun M. Global Cancer Facts & Figures 2007. American Cancer Society; 2007.
-
- Thomas M, Zhu A. Hepatocellular carcinoma: The need for progress. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(13):2892–2899. - PubMed
-
- Feitelson M, Ranganathan P, Clayton M, Zhang S. Partial characterization of the woodchuck tumor suppressor, p53, and its interaction with woodchuck hepatitis virus X antigen. Oncogene. 1997;1997(15):3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

