Decreased leukocyte accumulation and delayed Bordetella pertussis clearance in IL-6-/- mice
- PMID: 21398615
- PMCID: PMC3618952
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000594
Decreased leukocyte accumulation and delayed Bordetella pertussis clearance in IL-6-/- mice
Abstract
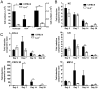
IL-6, a pleiotropic cytokine primarily produced by the innate immune system, has been implicated in the development of acquired immune responses, though its roles are largely undefined and may vary in the context of different diseases. Using a murine model of infection, we established that IL-6 influences the adaptive immune responses against the endemic human respiratory pathogen Bordetella pertussis. IL-6 was induced in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice by B. pertussis. IL-6(-/-) mice showed a protracted infectious course and were less efficiently protected by B. pertussis vaccination than wild-type mice. Abs from IL-6(-/-) mice, though lower in titer, efficiently reduced B. pertussis numbers in IL-6-sufficient mice. Pulmonary leukocyte recruitment and splenic or pulmonary T cell cytokine responses to B. pertussis, including Th1 and Th17 cytokine production, were lower in IL-6(-/-) mice than in wild-type mice. Adoptive transfer of immune wild-type CD4(+) cells ameliorated the defect of IL-6(-/-) mice in the control of B. pertussis numbers. Together, these results reveal the dysregulation of multiple aspects of adaptive immune responses in B. pertussis-infected IL-6(-/-) mice and suggest that IL-6 is involved in regulating Ab generation, pulmonary leukocyte accumulation, and T cell cytokine production in response to B. pertussis as well as the generation of effective vaccine-induced immunity against this pathogen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunological Signatures after Bordetella pertussis Infection Demonstrate Importance of Pulmonary Innate Immune Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0164027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164027. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711188 Free PMC article.
-
Azithromycin Clears Bordetella pertussis Infection in Mice but Also Modulates Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses and T Cell Memory.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 30;9:1764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01764. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30105030 Free PMC article.
-
Relative contribution of Th1 and Th17 cells in adaptive immunity to Bordetella pertussis: towards the rational design of an improved acellular pertussis vaccine.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003264. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003264. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23592988 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Programming of Innate Immune Cells in Response to Bordetella pertussis Infection and Vaccination.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1183:53-80. doi: 10.1007/5584_2019_404. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31432398 Review.
-
Pertussis: a matter of immune modulation.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011 May;35(3):441-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00257.x. Epub 2011 Jan 5. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21204863 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling Immune Evasion and Vaccine Limitations by Targeted Nasopharyngeal Bordetella pertussis Inoculation in Mice.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Aug;27(8):2107-2116. doi: 10.3201/eid2708.203566. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34286682 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of Human Airway Tissue Models Derived From Different Anatomical Sites to Bordetella pertussis and Its Virulence Factor Adenylate Cyclase Toxin.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Dec 23;11:797491. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.797491. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35059325 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Immunization with Acellular Pertussis Vaccines Results in Long-Term Immunity to Bordetella pertussis in Mice.Infect Immun. 2021 Feb 16;89(3):e00607-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00607-20. Print 2021 Feb 16. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33318136 Free PMC article.
-
Acellular pertussis vaccines protect against disease but fail to prevent infection and transmission in a nonhuman primate model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 14;111(2):787-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314688110. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24277828 Free PMC article.
-
Human metapneumovirus inhibits the IL-6-induced JAK/STAT3 signalling cascade in airway epithelium.J Gen Virol. 2014 Jan;95(Pt 1):26-37. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.055632-0. Epub 2013 Oct 10. J Gen Virol. 2014. PMID: 24114793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones SA. Directing transition from innate to acquired immunity: defining a role for IL-6. J Immunol. 2005;175:3463–3468. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:1–78. - PubMed
-
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

