MK-1775, a potent Wee1 inhibitor, synergizes with gemcitabine to achieve tumor regressions, selectively in p53-deficient pancreatic cancer xenografts
- PMID: 21389100
- PMCID: PMC3307341
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2580
MK-1775, a potent Wee1 inhibitor, synergizes with gemcitabine to achieve tumor regressions, selectively in p53-deficient pancreatic cancer xenografts
Abstract
Purpose: Investigate the efficacy and pharmacodynamic effects of MK-1775, a potent Wee1 inhibitor, in both monotherapy and in combination with gemcitabine (GEM) using a panel of p53-deficient and p53 wild-type human pancreatic cancer xenografts.
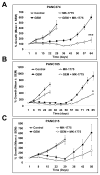
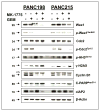
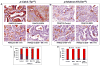
Experimental design: Nine individual patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts (6 with p53-deficient and 3 with p53 wild-type status) from the PancXenoBank collection at Johns Hopkins were treated with MK-1775, GEM, or GEM followed 24 hour later by MK-1775, for 4 weeks. Tumor growth rate/regressions were calculated on day 28. Target modulation was assessed by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry.
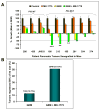
Results: MK-1775 treatment led to the inhibition of Wee1 kinase and reduced inhibitory phosphorylation of its substrate Cdc2. MK-1775, when dosed with GEM, abrogated the checkpoint arrest to promote mitotic entry and facilitated tumor cell death as compared to control and GEM-treated tumors. MK-1775 monotherapy did not induce tumor regressions. However, the combination of GEM with MK-1775 produced robust antitumor activity and remarkably enhanced tumor regression response (4.01-fold) compared to GEM treatment in p53-deficient tumors. Tumor regrowth curves plotted after the drug treatment period suggest that the effect of the combination therapy is longer-lasting than that of GEM. None of the agents produced tumor regressions in p53 wild-type xenografts.
Conclusions: These results indicate that MK-1775 selectively synergizes with GEM to achieve tumor regressions, selectively in p53-deficient pancreatic cancer xenografts.
©2011 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small-molecule inhibition of Wee1 kinase by MK-1775 selectively sensitizes p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Nov;8(11):2992-3000. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0463. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19887545
-
Dual inhibition of the PI3K and MAPK pathways enhances nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine chemotherapy response in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2019 Sep 10;459:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.05.037. Epub 2019 May 30. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31153980
-
Preclinical evaluation of the WEE1 inhibitor MK-1775 as single-agent anticancer therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Aug;12(8):1442-52. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0025. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23699655
-
Abrogation of the G2 checkpoint by inhibition of Wee-1 kinase results in sensitization of p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;5(3):186-91. doi: 10.2174/157488410791498824. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20406171 Review.
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interferon-beta enhances sensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Sep 23;20(1):913. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07420-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32967656 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Tumor Effects of Wee1 Kinase Inhibitor with Radiotherapy in Human Cervical Cancer.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 28;9(1):15394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51959-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31659268 Free PMC article.
-
ATR and CDK4/6 inhibition target the growth of methotrexate-resistant choriocarcinoma.Oncogene. 2022 Apr;41(18):2540-2554. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02251-8. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35301407 Free PMC article.
-
HuR posttranscriptionally regulates WEE1: implications for the DNA damage response in pancreatic cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 15;74(4):1128-40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1915. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24536047 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic antitumor interactions between MK-1775 and panobinostat in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):656-68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.015. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25458954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Burris HA, 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2403–13. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–6. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Vervenne WL, Bennouna J, et al. Phase III trial of bevacizumab in combination with gemcitabine and erlotinib in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2231–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

