Intracranial atherosclerosis as a contributing factor to Alzheimer's disease dementia
- PMID: 21388893
- PMCID: PMC3117084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.08.228
Intracranial atherosclerosis as a contributing factor to Alzheimer's disease dementia
Abstract
Background: A substantial body of evidence collected from epidemiologic, correlative, and experimental studies strongly associates atherosclerotic vascular disease (AVD) with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Depending on the precise interrelationship between AVD and AD, systematic application of interventions used to maintain vascular health and function as a component of standard AD therapy offers the prospect of mitigating the presently inexorable course of dementia. To assess this hypothesis, it is vital to rigorously establish the measures of AVD that are most strongly associated with an AD diagnosis.
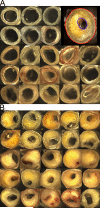
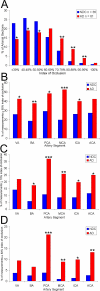
Methods: A precise neuropathological diagnosis was established for all subjects, using a battery of genetic, clinical, and histological methods. The severity of atherosclerosis in the circle of Willis was quantified by direct digitized measurement of arterial occlusion in postmortem specimens and was compared between AD and nondemented control groups by calculating a corresponding index of occlusion.
Results: Atherosclerotic occlusion of the circle of Willis arteries was more extensive in the AD group than in the nondemented control group. Statistically significant differences were also observed between control and AD groups with regard to Braak stage, total plaque score, total neurofibrillary tangle score, total white matter rarefaction score, brain weight, Mini-Mental State Examination scores, and apolipoprotein E allelic frequencies.
Conclusions: Our results, combined with a consideration of the multifaceted effects of impaired cerebral circulation, suggest an immediate need for prospective clinical trials to assess the efficacy of AD prevention using antiatherosclerotic agents.
Copyright © 2011 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circle of Willis atherosclerosis: association with Alzheimer's disease, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.Acta Neuropathol. 2007 Jan;113(1):13-21. doi: 10.1007/s00401-006-0136-y. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Acta Neuropathol. 2007. PMID: 17021755
-
Circle of willis atherosclerosis is a risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Nov 1;23(11):2055-62. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000095973.42032.44. Epub 2003 Sep 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. PMID: 14512367
-
Large vessel cerebral atherosclerosis is not in direct association with neuropathological lesions of Alzheimer's disease.Eur Neurol. 2009;62(2):93-8. doi: 10.1159/000222779. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Eur Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19521084
-
Atherosclerosis, vascular amyloidosis and brain hypoperfusion in the pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease.Neurol Res. 2004 Jul;26(5):525-39. doi: 10.1179/016164104225017668. Neurol Res. 2004. PMID: 15265270 Review.
-
Pathologic correlates of nondemented aging, mild cognitive impairment, and early-stage Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2001 Oct;17(2):101-18. doi: 10.1385/jmn:17:2:101. J Mol Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11816784 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease With Brain β-Amyloid Deposition: Secondary Analysis of the ARIC Study.JAMA Neurol. 2020 Mar 1;77(3):350-357. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4339. JAMA Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31860001 Free PMC article.
-
The total alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Franch improve cognitive deficits in type 2 diabetic rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Aug 31;12:2695-2706. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S171025. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30214157 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and subcortical cerebrovascular resistance index in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;36(4):689-98. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130086. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23666173 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Coronary Artery Calcification and Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Hippocampal Volume: An Analysis From the Dallas Heart Study.J Acad Consult Liaison Psychiatry. 2023 May-Jun;64(3):218-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jaclp.2023.01.007. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J Acad Consult Liaison Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36681150 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial atherosclerosis and dementia: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study.Neurology. 2017 Apr 18;88(16):1556-1563. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003837. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28330958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beach TG, Wilson JR, Sue LI, Newell A, Poston M, Cisneros R, et al. Circle of Willis atherosclerosis: association with Alzheimer's disease, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Roher AE, Esh C, Kokjohn TA, Kalback W, Luehrs DC, Seward JD, et al. Circle of Willis atherosclerosis is a risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:2055–62. - PubMed
-
- Kalback W, Esh C, Castano EM, Rahman A, Kokjohn T, Luehrs DC, et al. Atherosclerosis, vascular amyloidosis and brain hypoperfusion in the pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Res. 2004;26:525–39. - PubMed
-
- Roher AE, Esh C, Rahman A, Kokjohn TA, Beach TG. Atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries in Alzheimer disease. Stroke. 2004;35:2623–27. - PubMed
-
- Honig LS, Kukull W, Mayeux R. Atherosclerosis and AD: analysis of data from the US National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center. Neurology. 2005;64:494–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

