Identification of novel Ras-cooperating oncogenes in Drosophila melanogaster: a RhoGEF/Rho-family/JNK pathway is a central driver of tumorigenesis
- PMID: 21368274
- PMCID: PMC3120157
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.111.127910
Identification of novel Ras-cooperating oncogenes in Drosophila melanogaster: a RhoGEF/Rho-family/JNK pathway is a central driver of tumorigenesis
Abstract
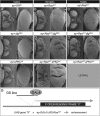
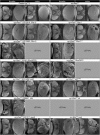
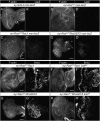
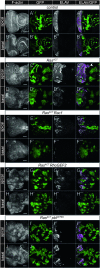
We have shown previously that mutations in the apico-basal cell polarity regulators cooperate with oncogenic Ras (Ras(ACT)) to promote tumorigenesis in Drosophila melanogaster and mammalian cells. To identify novel genes that cooperate with Ras(ACT) in tumorigenesis, we carried out a genome-wide screen for genes that when overexpressed throughout the developing Drosophila eye enhance Ras(ACT)-driven hyperplasia. Ras(ACT)-cooperating genes identified were Rac1 Rho1, RhoGEF2, pbl, rib, and east, which encode cell morphology regulators. In a clonal setting, which reveals genes conferring a competitive advantage over wild-type cells, only Rac1, an activated allele of Rho1 (Rho1(ACT)), RhoGEF2, and pbl cooperated with Ras(ACT), resulting in reduced differentiation and large invasive tumors. Expression of RhoGEF2 or Rac1 with Ras(ACT) upregulated Jun kinase (JNK) activity, and JNK upregulation was essential for cooperation. However, in the whole-tissue system, upregulation of JNK alone was not sufficient for cooperation with Ras(ACT), while in the clonal setting, JNK upregulation was sufficient for Ras(ACT)-mediated tumorigenesis. JNK upregulation was also sufficient to confer invasive growth of Ras(V12)-expressing mammalian MCF10A breast epithelial cells. Consistent with this, HER2(+) human breast cancers (where human epidermal growth factor 2 is overexpressed and Ras signaling upregulated) show a significant correlation with a signature representing JNK pathway activation. Moreover, our genetic analysis in Drosophila revealed that Rho1 and Rac are important for the cooperation of RhoGEF2 or Pbl overexpression and of mutants in polarity regulators, Dlg and aPKC, with Ras(ACT) in the whole-tissue context. Collectively our analysis reveals the importance of the RhoGEF/Rho-family/JNK pathway in cooperative tumorigenesis with Ras(ACT).
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Drosophila, RhoGEF2 cooperates with activated Ras in tumorigenesis through a pathway involving Rho1-Rok-Myosin-II and JNK signalling.Dis Model Mech. 2013 May;6(3):661-78. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010066. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23324326 Free PMC article.
-
Scribble mutants promote aPKC and JNK-dependent epithelial neoplasia independently of Crumbs.BMC Biol. 2009 Sep 24;7:62. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-62. BMC Biol. 2009. PMID: 19778415 Free PMC article.
-
Src Cooperates with Oncogenic Ras in Tumourigenesis via the JNK and PI3K Pathways in Drosophila epithelial Tissue.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 27;19(6):1585. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061585. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29861494 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic and pro-proliferation functions of the JNK pathway of Drosophila: roles in cell competition, tumorigenesis and regeneration.Open Biol. 2019 Mar 29;9(3):180256. doi: 10.1098/rsob.180256. Open Biol. 2019. PMID: 30836847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pebble GTP exchange factor and the control of cytokinesis.Cell Struct Funct. 2001 Dec;26(6):619-26. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.619. Cell Struct Funct. 2001. PMID: 11942617 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling of residual breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy identifies DUSP4 deficiency as a mechanism of drug resistance.Nat Med. 2012 Jul;18(7):1052-9. doi: 10.1038/nm.2795. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22683778 Free PMC article.
-
Src42A modulates tumor invasion and cell death via Ben/dUev1a-mediated JNK activation in Drosophila.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 17;4(10):e864. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.392. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24136228 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic models of apoptosis-induced proliferation decipher activation of JNK and identify a requirement of EGFR signaling for tissue regenerative responses in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan 30;10(1):e1004131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004131. eCollection 2014 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24497843 Free PMC article.
-
Development of EHop-016: a small molecule inhibitor of Rac.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A(Pt A):117-46. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00006-3. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Drosophila to uncover the role of organismal physiology and the tumor microenvironment in cancer.Trends Cancer. 2024 Apr;10(4):289-311. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2024.01.007. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Trends Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38350736 Review.
References
-
- Adachi-Yamada T., O'Connor M. B., 2004. Mechanisms for removal of developmentally abnormal cells: cell competition and morphogenetic apoptosis. J. Biochem. 136: 13–17 - PubMed
-
- Aigaki T., Ohsako T., Toba G., Seong K., Matsuo T., 2001. The gene search system: its application to functional genomics in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurogenet. 15: 169–178 - PubMed
-
- Baonza A., Freeman M., 2005. Control of cell proliferation in the Drosophila eye by Notch signaling. Dev. Cell 8: 529–539 - PubMed
-
- Barrett K., Leptin M., Settleman J., 1997. The Rho GTPase and a putative RhoGEF mediate a signaling pathway for the cell shape changes in Drosophila gastrulation. Cell 91: 905–915 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

