Apoptosis of human melanoma cells induced by inhibition of B-RAFV600E involves preferential splicing of bimS
- PMID: 21364673
- PMCID: PMC3032346
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2010.48
Apoptosis of human melanoma cells induced by inhibition of B-RAFV600E involves preferential splicing of bimS
Abstract
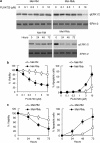
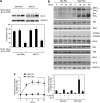
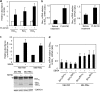
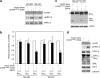
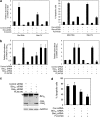
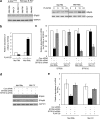
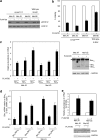
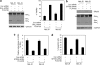
Bim is known to be critical in killing of melanoma cells by inhibition of the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. However, the potential role of the most potent apoptosis-inducing isoform of Bim, Bim(S), remains largely unappreciated. Here, we show that inhibition of the mutant B-RAF(V600E) triggers preferential splicing to produce Bim(S), which is particularly important in induction of apoptosis in B-RAF(V600E) melanoma cells. Although the specific B-RAF(V600E) inhibitor PLX4720 upregulates all three major isoforms of Bim, Bim(EL), Bim(L), and Bim(S), at the protein and mRNA levels in B-RAF(V600E) melanoma cells, the increase in the ratios of Bim(S) mRNA to Bim(EL) and Bim(L) mRNA indicates that it favours Bim(S) splicing. Consistently, enforced expression of B-RAF(V600E) in wild-type B-RAF melanoma cells and melanocytes inhibits Bim(S) expression. The splicing factor SRp55 appears necessary for the increase in Bim(S) splicing, as SRp55 is upregulated, and its inhibition by small interfering RNA blocks induction of Bim(S) and apoptosis induced by PLX4720. The PLX4720-induced, SRp55-mediated increase in Bim(S) splicing is also mirrored in freshly isolated B-RAF(V600E) melanoma cells. These results identify a key mechanism for induction of apoptosis by PLX4720, and are instructive for sensitizing melanoma cells to B-RAF(V600E) inhibitors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oncogenic BRAF(V600E) inhibits BIM expression to promote melanoma cell survival.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008 Oct;21(5):534-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00491.x. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008. PMID: 18715233 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc-induced modulation of SRSF6 activity alters Bim splicing to promote generation of the most potent apoptotic isoform BimS.FEBS J. 2013 Jul;280(14):3313-27. doi: 10.1111/febs.12318. Epub 2013 Jun 3. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23648111
-
Evidence for upregulation of Bim and the splicing factor SRp55 in melanoma cells from patients treated with selective BRAF inhibitors.Melanoma Res. 2012 Jun;22(3):244-51. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328353eff2. Melanoma Res. 2012. PMID: 22516966
-
PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through the suppression of BIM expression.Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 1;71(7):2750-60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2954. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21317224 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in B-RAF inhibitors as anticancer agents.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Mar;120:105597. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105597. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35033817 Review.
Cited by
-
RAF265 inhibits the growth of advanced human melanoma tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 15;18(8):2184-98. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1122. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22351689 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and AXIN1 regulate apoptosis triggered by inhibition of the mutant kinase BRAFV600E in human melanoma.Sci Signal. 2012 Jan 10;5(206):ra3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002274. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22234612 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and mechanisms of aberrant alternative splicing in melanoma - implications for targeted therapy and immunotherapy resistance.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Mar 10;24(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03280-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38462618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of PP2A is critical for protection of melanoma cells upon endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Jun 28;3(6):e337. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.79. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22739989 Free PMC article.
-
Bim polymorphisms: influence on function and response to treatment in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 15;19(18):5240-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1215. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23908358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Sosman J, Kim K, Ribas A, McArthur A, et al. Phase I study of PLX4032: Proof of concept for V600E BRAF mutation as a therapeutic target in human cancer J Clin Oncol 200927Abstract 9000.
-
- Chapman P, Puzanov I, Sosman J, Kim K, Ribas A, McArthur A, et al. Early efficacy signal demonstrated in advanced melanoma in a phase I trial of the oncogenic BRAF-selective inhibitor PLX4032. Eur J Cancer Suppl. 2009;7:5.
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

