FGF2 sustains NANOG and switches the outcome of BMP4-induced human embryonic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 21362572
- PMCID: PMC3052735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.01.001
FGF2 sustains NANOG and switches the outcome of BMP4-induced human embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
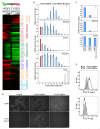
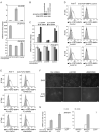
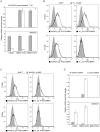
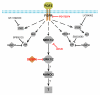
Here, we show that as human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) exit the pluripotent state, NANOG can play a key role in determining lineage outcome. It has previously been reported that BMPs induce differentiation of human ESCs into extraembryonic lineages. Here, we find that FGF2, acting through the MEK-ERK pathway, switches BMP4-induced human ESC differentiation outcome to mesendoderm, characterized by the uniform expression of T (brachyury) and other primitive streak markers. We also find that MEK-ERK signaling prolongs NANOG expression during BMP-induced differentiation, that forced NANOG expression results in FGF-independent BMP4 induction of mesendoderm, and that knockdown of NANOG greatly reduces T induction. Together, our results demonstrate that FGF2 signaling switches the outcome of BMP4-induced differentiation of human ESCs by maintaining NANOG levels through the MEK-ERK pathway.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGF inhibition directs BMP4-mediated differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to syncytiotrophoblast.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Nov 1;21(16):2987-3000. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0099. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22724507 Free PMC article.
-
BRACHYURY and CDX2 mediate BMP-induced differentiation of human and mouse pluripotent stem cells into embryonic and extraembryonic lineages.Cell Stem Cell. 2011 Aug 5;9(2):144-55. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.015. Cell Stem Cell. 2011. PMID: 21816365 Free PMC article.
-
Brf1 posttranscriptionally regulates pluripotency and differentiation responses downstream of Erk MAP kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 29;111(17):E1740-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320873111. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24733888 Free PMC article.
-
Model systems for studying trophoblast differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Sep;349(3):809-24. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1371-2. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22427062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specification of trophoblast from embryonic stem cells exposed to BMP4.Biol Reprod. 2018 Jul 1;99(1):212-224. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy070. Biol Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29579154 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling networks in human pluripotent stem cells.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;25(2):241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.09.005. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23092754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule-assisted, line-independent maintenance of human pluripotent stem cells in defined conditions.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041958. Epub 2012 Jul 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22860038 Free PMC article.
-
Differential BMP signaling controls formation and differentiation of multipotent preplacodal ectoderm progenitors from human embryonic stem cells.Dev Biol. 2013 Jul 15;379(2):208-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.023. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23643939 Free PMC article.
-
A Primate lncRNA Mediates Notch Signaling during Neuronal Development by Sequestering miRNA.Neuron. 2016 Jun 15;90(6):1174-1188. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27263970 Free PMC article.
-
A novel self-organizing embryonic stem cell system reveals signaling logic underlying the patterning of human ectoderm.Development. 2019 Oct 17;146(20):dev179093. doi: 10.1242/dev.179093. Development. 2019. PMID: 31519692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arkell RS, Dickinson RJ, Squires M, Hayat S, Keyse SM, Cook SJ. DUSP6/MKP-3 inactivates ERK1/2 but fails to bind and inactivate ERK5. Cell Signal. 2008;20:836–843. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L, Hughes O, Yung S, Hyslop L, Stewart R, Wappler I, Peters H, Walter T, Stojkovic P, Evans J, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFkappabeta signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1894–1913. - PubMed
-
- Brons IG, Smithers LE, Trotter MW, Rugg-Gunn P, Sun B, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Howlett SK, Clarkson A, Ahrlund-Richter L, Pedersen RA, et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, Nichols J, Lee S, Tweedie S, Smith A. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2003;113:643–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

