MHCI negatively regulates synapse density during the establishment of cortical connections
- PMID: 21358642
- PMCID: PMC3251641
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2764
MHCI negatively regulates synapse density during the establishment of cortical connections
Abstract
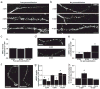
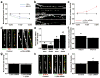
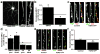
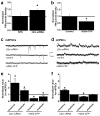
Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) molecules modulate activity-dependent refinement and plasticity. We found that MHCI also negatively regulates the density and function of cortical synapses during their initial establishment both in vitro and in vivo. MHCI molecules are expressed on cortical neurons before and during synaptogenesis. In vitro, decreasing surface MHCI (sMHCI) on neurons increased glutamatergic and GABAergic synapse density, whereas overexpression decreased it. In vivo, synapse density was higher throughout development in β2m(-/-) mice. MHCI also negatively regulated the strength of excitatory, but not inhibitory, synapses and controlled the balance of excitation and inhibition onto cortical neurons. sMHCI levels were modulated by activity and were necessary for activity to negatively regulate glutamatergic synapse density. Finally, acute changes in sMHCI and activity altered synapse density exclusively during early postnatal development. These results identify a previously unknown function for immune proteins in the negative regulation of the initial establishment and function of cortical connections.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MHCI requires MEF2 transcription factors to negatively regulate synapse density during development and in disease.J Neurosci. 2013 Aug 21;33(34):13791-804. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2366-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23966700 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CNS synapses by neuronal MHC class I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 17;104(16):6828-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702023104. Epub 2007 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17420446 Free PMC article.
-
MHC class I limits hippocampal synapse density by inhibiting neuronal insulin receptor signaling.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 27;34(35):11844-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4642-12.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25164678 Free PMC article.
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I proteins in brain development and plasticity.Trends Neurosci. 2012 Nov;35(11):660-70. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Trends Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22939644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salient features of synaptic organisation in the cerebral cortex.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998 May;26(2-3):113-35. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(97)00061-1. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998. PMID: 9651498 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic profiles of hiPSC-derived dopamine neurons from clinically discordant brothers with identical PRKN deletions.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022 Jun 29;8(1):84. doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00346-3. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022. PMID: 35768426 Free PMC article.
-
MHC class I in dopaminergic neurons suppresses relapse to reward seeking.Sci Adv. 2018 Mar 14;4(3):eaap7388. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap7388. eCollection 2018 Mar. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 29546241 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation analysis of the autistic brain reveals multiple dysregulated biological pathways.Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Sep 2;4(9):e433. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.70. Transl Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25180572 Free PMC article.
-
The nonclassical MHC class I Qa-1 expressed in layer 6 neurons regulates activity-dependent plasticity via microglial CD94/NKG2 in the cortex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 7;119(23):e2203965119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2203965119. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35648829 Free PMC article.
-
The similar expression pattern of MHC class I molecules in human and mouse cerebellar cortex.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jan;39(1):180-6. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1204-z. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24272393
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

