Functional identification of optimized RNAi triggers using a massively parallel sensor assay
- PMID: 21353615
- PMCID: PMC3130540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.008
Functional identification of optimized RNAi triggers using a massively parallel sensor assay
Abstract
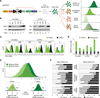
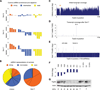
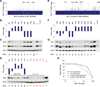
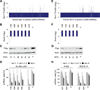
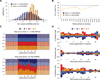
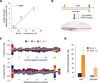
Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) provide powerful experimental tools by enabling stable and regulated gene silencing through programming of endogenous microRNA pathways. Since requirements for efficient shRNA biogenesis and target suppression are largely unknown, many predicted shRNAs fail to efficiently suppress their target. To overcome this barrier, we developed a "Sensor assay" that enables the biological identification of effective shRNAs at large scale. By constructing and evaluating 20,000 RNAi reporters covering every possible target site in nine mammalian transcripts, we show that our assay reliably identifies potent shRNAs that are surprisingly rare and predominantly missed by existing algorithms. Our unbiased analyses reveal that potent shRNAs share various predicted and previously unknown features associated with specific microRNA processing steps, and suggest a model for competitive strand selection. Together, our study establishes a powerful tool for large-scale identification of highly potent shRNAs and provides insights into sequence requirements of effective RNAi.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Construction of simple and efficient DNA vector-based short hairpin RNA expression systems for specific gene silencing in mammalian cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;408:223-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-547-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18314586
-
Endogenous spacing enables co-processing of microRNAs and efficient combinatorial RNAi.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Jun 21;2(7):100239. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100239. eCollection 2022 Jul 18. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 35880017 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation of off-target effects from vector-encoded shRNAs via codelivered RNA decoys.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 28;112(30):E4007-16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1510476112. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26170322 Free PMC article.
-
Short hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;942:205-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-119-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23027054 Review.
-
Artificial miRNAs as therapeutic tools: Challenges and opportunities.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 Jul;12(4):e1640. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1640. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 33386705 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunodeficiency and autoimmune enterocolopathy linked to NFAT5 haploinsufficiency.J Immunol. 2015 Mar 15;194(6):2551-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401463. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25667416 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a Novel Oncolytic Adenovirus Silencing SYVN1.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 6;23(23):15430. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315430. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499754 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial microRNA guide strand selection from duplexes with no mismatches shows a purine-rich preference for virus- and non-virus-based expression vectors in plants.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun;20(6):1069-1084. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13786. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35113475 Free PMC article.
-
Development of siRNA payloads to target KRAS-mutant cancer.Cancer Discov. 2014 Oct;4(10):1182-1197. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0900. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Cancer Discov. 2014. PMID: 25100204 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo transfection system for inducible gene expression and gene silencing in murine hepatocytes.J Gene Med. 2017 Jan;19(1-2):10.1002/jgm.2940. doi: 10.1002/jgm.2940. J Gene Med. 2017. PMID: 28009940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ameres SL, Martinez J, Schroeder R. Molecular basis for target RNA recognition and cleavage by human RISC. Cell. 2007;130:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

